RCA for Vacuum Circuit Breaker Failure in Electrical Systems
A vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) is a crucial device in petrochemical plants used to protect electrical systems by interrupting high-voltage circuits during fault conditions, such as short circuits or overloads. It operates by opening contacts in a vacuum chamber, which ensures that the arc created when the circuit breaks is quickly extinguished due to the absence of gas or other mediums that could maintain the arc. This technology is valued for its reliability, longevity, and low maintenance. In the high-risk environment of a petrochemical plant, VCBs protect critical equipment like motors, transformers, and switchgear, ensuring stable operations and minimizing downtime.
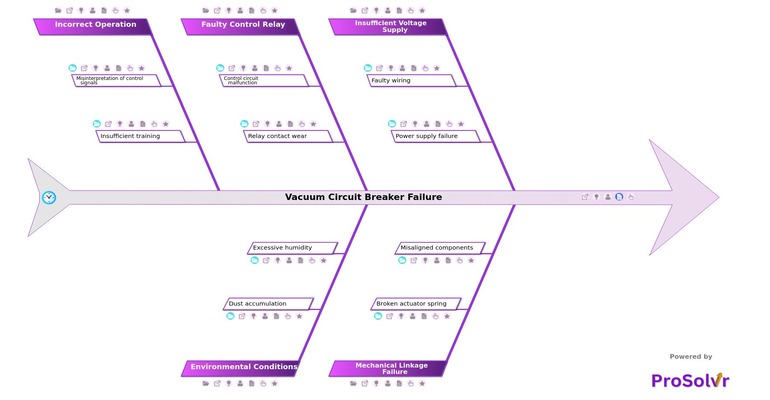
However, malfunctions in vacuum circuit breakers can lead to significant problems, such as equipment damage, power outages, or even fires. Issues might arise from worn contacts, improper maintenance, mechanical failures, or environmental factors like dust and moisture. These failures can disrupt production, cause safety hazards, and incur financial losses. Identifying the exact cause of a malfunction quickly is crucial to minimize downtime and prevent recurrence of similar issues.
Root cause analysis (RCA) using a fishbone diagram can systematically address the malfunction of a VCB. By categorizing potential causes into key areas like human factors, materials, equipment, processes, and environmental conditions, the fishbone diagram helps teams visually break down the problem. For instance, if a VCB failure occurred due to contact wear, this could be traced back to inadequate maintenance procedures or poor-quality materials. Analyzing each possible root cause allows engineers to not only fix the immediate issue but also implement preventive measures, such as improving maintenance protocols or upgrading equipment, reducing the risk of future failures.
Who can learn from the Vacuum Circuit Breaker Failure template?
Root cause analysis (RCA) of vacuum circuit breaker failure in electrical systems offers valuable insights to various stakeholders.
- Maintenance Teams: They can use insights from VCB failure templates to improve inspection, repair schedules, and maintenance procedures to prevent future malfunctions.
- Operations Personnel: Understanding the failures helps operators recognize early warning signs of potential issues and follow proper protocols to avoid catastrophic failures during daily operations.
- Engineering Teams: Engineers can study failure modes to design more robust systems, optimize electrical networks, and suggest necessary upgrades or modifications to circuit breakers.
- Safety and Compliance Teams: They can learn how VCB failures impact plant safety and compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring necessary precautions are in place to mitigate electrical hazards.
- Procurement Teams: Insights from failures can guide procurement decisions, ensuring that high-quality VCBs and replacement parts are sourced, along with maintaining relationships with reliable vendors.
- Training and Development Teams: They can incorporate lessons from past failures into training modules to equip employees with the knowledge needed to identify risks, manage equipment better, and respond effectively to issues.
Why use this template?
Using root cause analysis (RCA) for vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) failures in petrochemical plants offers significant benefits by enabling a structured approach to identifying and addressing the underlying causes of malfunctions. RCA helps prevent recurring issues by thoroughly investigating not just the immediate symptoms of the failure but also the deeper, systemic causes such as poor maintenance practices, substandard materials, or environmental conditions. This proactive problem-solving method reduces downtime, enhances safety, and improves the reliability of electrical systems. By implementing corrective and preventive measures based on RCA findings, plants can optimize maintenance strategies, reduce repair costs, and ensure smoother, uninterrupted operations, ultimately safeguarding both equipment and personnel.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.