Root Cause Analysis of Transmission Failure in EVs
Electric vehicles (EVs) use simpler transmission systems, typically relying on single-speed gearboxes. However, transmission failure can still occur, impacting performance, efficiency, and safety. These issues might stem from manufacturing defects, overheating, lubrication problems, component wear and tear, or software glitches in the transmission control system. While EV transmissions are generally more reliable due to fewer moving parts, the integration of electrical and mechanical systems presents unique challenges, such as synchronization problems between electric motors and the transmission, or faulty sensors and actuators.
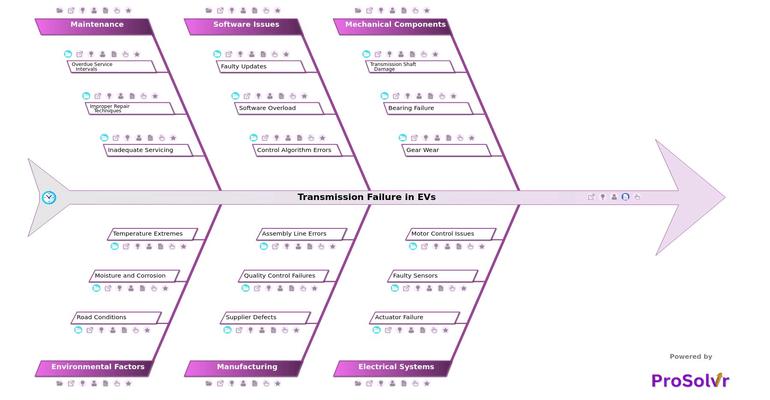
A fishbone diagram (Ishikawa diagram) is a valuable tool for conducting root cause analysis (RCA) of EV transmission failure. By categorizing potential causes into major groups like mechanical, electrical, and software-related factors, the diagram allows for a structured investigation. This approach facilitates the identification of root causes such as design flaws or improper component integration, helping teams focus on specific corrective actions.
Applying Six Sigma principles within this structured RCA process enables teams to trace the source of transmission failures. By identifying the underlying causes and implementing corrective actions, organizations can prevent similar issues in the future, improving EV transmission reliability and extending system lifespan.
Who can learn from the Transmission Failure in EVs template?
- Automotive Engineers and Designers: Improve future EV transmission designs by understanding root causes like mechanical wear, software issues, or synchronization failures.
- Maintenance Technicians: Learn to recognize early signs of transmission failure, enhance lubrication and maintenance routines, and prevent major breakdowns.
- Quality Assurance and Control Teams: Tighten quality control measures during production by identifying potential transmission issues before vehicles leave the factory.
- Software and Control System Developers: Discover how software glitches affect transmission performance and work on improving algorithms that manage gear shifts and motor synchronization.
- Automotive Supply Chain Managers: Reassess supplier performance and material quality based on the root cause analysis of transmission components.
- EV Manufacturers and Executives: Use transmission failure insights to drive strategic decisions in technology investments and improve overall product reliability.
Why use this template?
ProSolvr, an AI-powered root cause analysis tool, simplifies the diagnostic process for transmission failures in EVs. By utilizing fishbone diagrams to systematically break down and investigate potential causes, this fishbone analysis helps teams accelerate troubleshooting efforts. This enables the development of preventive strategies that minimize downtime. This template could be the starting point for teams to resolve issues efficiently, enhancing the overall reliability of EV transmission systems.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effective diagnosis and resolution of transmission failures in EVs, ensuring vehicle reliability and safety.