Root Cause Analysis of Engine Stalling in Heavy-Duty Trucks
Engine stalling in heavy-duty trucks is a significant issue that can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards. Common causes of engine stalling include fuel delivery problems, electrical system malfunctions, and air intake issues. Heavy-duty trucks operating under substantial loads or in extreme conditions are particularly vulnerable to engine stalls, which can disrupt delivery schedules and contribute to wear and tear on other vehicle components.
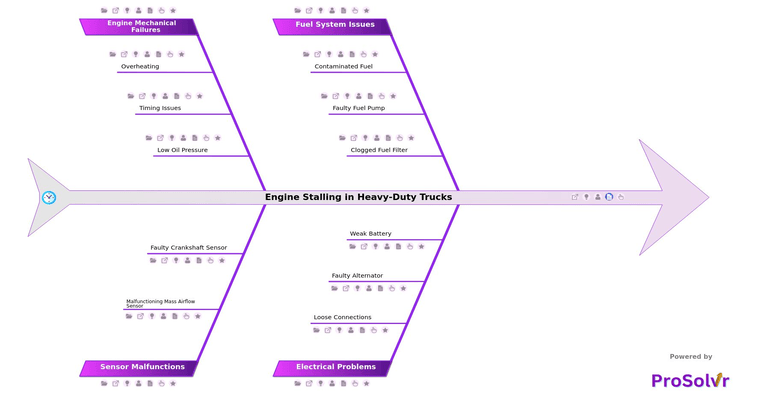
The complexity of modern truck engines makes it challenging to pinpoint the exact cause of stalling without a systematic approach. A root cause analysis (RCA) using a fishbone diagram (Ishikawa diagram) is an effective method for addressing engine stalling in heavy-duty trucks. The fishbone diagram helps break down the problem into various categories, allowing teams to systematically evaluate potential causes and identify the root cause of engine stalling.
Once the root cause is determined through fishbone analysis, targeted corrective actions can be developed to resolve the underlying issues. This structured approach not only addresses the immediate problem but also reduces the risk of recurrence by tackling factors contributing to engine failure. Moreover, tracking these issues over time can enhance overall truck fleet performance and reliability, ensuring minimal downtime and improved operational efficiency.
Fleet maintenance teams are essential in this process, as they are responsible for ensuring that trucks are in optimal working condition. By using the fishbone diagram, they can systematically diagnose engine stalling issues, leading to more efficient repairs and preventive maintenance planning. Truck drivers can also benefit from understanding the potential causes of engine stalling and recognizing early warning signs. This knowledge aids them in effectively communicating issues to maintenance crews, helping to prevent roadside breakdowns.
Truck manufacturers can leverage insights from RCA to improve the design and durability of fuel and electrical systems, thereby reducing the likelihood of stalling issues in future truck models. Logistics and operations managers can better anticipate and mitigate disruptions caused by engine stalling, ultimately improving fleet performance and customer service. Additionally, safety and compliance officers can utilize root cause analysis to develop guidelines and policies that ensure trucks are maintained and operated safely, thereby reducing the risk of accidents due to engine failure.
ProSolvr, being a generative AI-powered RCA tool, can significantly enhance root cause analysis for stalling engine issues in trucks by streamlining problem-solving techniques and facilitating collaboration among teams. It enables a systematic approach to identifying potential causes of engine stalling, encouraging comprehensive analysis without relying on extensive datasets. This accelerates troubleshooting, develops effective preventive strategies, and minimizes downtime, ultimately boosting overall fleet reliability and performance.
Who can learn from the Engine Stalling in Heavy Duty Trucks template?
- Fleet Maintenance Teams: Responsible for ensuring optimal truck performance, these teams can use the fishbone diagram to systematically diagnose engine stalling issues, leading to more efficient repairs and preventive maintenance.
- Truck Drivers: Understanding potential causes of engine stalling and recognizing early warning signs can help drivers communicate issues effectively to maintenance teams and prevent breakdowns.
- Truck Manufacturers: Engineers and quality control teams can leverage these insights to improve the design of fuel and electrical systems, reducing the likelihood of stalling in future truck models.
- Logistics and Operations Managers: These managers can use the analysis to anticipate and mitigate disruptions, improving fleet efficiency and customer service by addressing engine stalling causes.
- Safety and Compliance Officers: With a clearer understanding of root causes, safety officers can help develop guidelines to ensure trucks are maintained and operated safely, reducing the risk of accidents due to engine failure.
Why use this template?
Generative AI (Gen AI) enhances root cause analysis (RCA) for truck engine stalling by providing structured problem-solving techniques and visual tools, such as fishbone diagrams. ProSolvr facilitates a systematic approach to identifying potential causes of engine stalling, encouraging collaboration among teams and ensuring that all angles are considered. This not only accelerates the troubleshooting process but also helps develop effective preventive strategies. By streamlining the RCA process, ProSolvr minimizes downtime and boosts overall fleet reliability and performance.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effective diagnosis and resolution of all your automotive issues, ensuring comprehensive vehicle safety.