RCA of Shortage of Medicines
Shortage of medicines is a critical challenge in the pharmaceutical industry, directly impacting patient care, treatment continuity, and public health outcomes. When essential drugs are unavailable, healthcare providers struggle to maintain treatment protocols, often resulting in delayed therapies, substitution with less effective alternatives, or even adverse health consequences. Beyond patient impact, shortages create significant operational and reputational challenges for pharmaceutical companies, including disrupted supply chains, increased regulatory scrutiny, and financial losses due to unmet market demand.
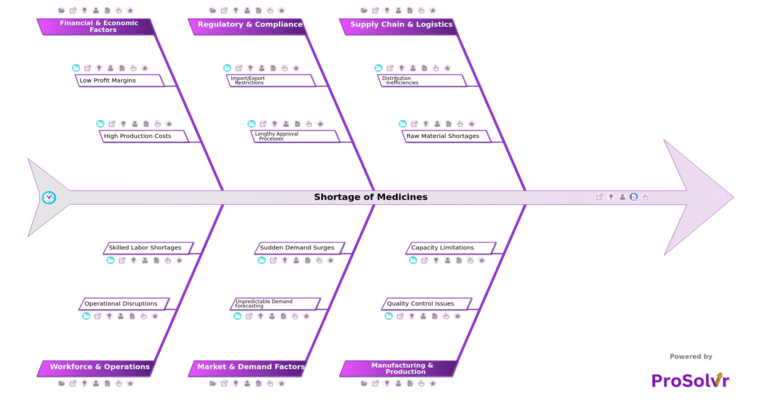
Medicine shortages arise from multiple interconnected factors spanning supply chain, manufacturing, regulatory, workforce, and market dynamics. For example, distribution inefficiencies such as transportation disruptions and poor inventory tracking can prevent timely delivery to healthcare facilities. Raw material shortages, often linked to export restrictions on APIs or dependence on single suppliers, further constrain production capacity. Manufacturing challenges including failed regulatory inspections, product recalls, limited production lines, and outdated facilities exacerbate supply risks.
Regulatory and compliance hurdles also contribute, with import/export restrictions, sudden policy changes, country-specific trade barriers, lengthy approval cycles, and complex documentation requirements delaying market availability. On the market side, unpredictable demand forecasting, lack of real-time data, panic buying, and demand surges during epidemics or pandemics often overwhelm supply systems. Financial and economic pressures, such as price controls, low profit margins, high production costs, and raw material price fluctuations, add further strain. Finally, workforce and operational challenges including absenteeism during pandemics, labor strikes, high staff turnover, and shortage of trained technicians amplify disruption risks.
A GEN-AI powered root cause analysis (RCA), structured through a fishbone diagram and aligned with Six Sigma principles, can be invaluable in addressing these shortages. By systematically analyzing why a shortage occurred and categorizing causes across supply chain, manufacturing, compliance, market, financial, and workforce dimensions, RCA ensures a comprehensive understanding of the underlying issues. This structured approach supports the design of targeted Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA), addressing root causes such as failed inspections, transport disruptions, or skilled labor shortages, rather than only mitigating surface-level symptoms.
Applications like ProSolvr, which integrate fishbone diagram-based RCA with GEN-AI capabilities, take this a step further. ProSolvr enables pharmaceutical teams to map complex interdependencies between causes, visualize bottlenecks, and prioritize corrective measures. With clear visual insights and AI-driven recommendations, organizations can ensure that lessons learned from one shortage are systematically applied to prevent recurrence. This not only strengthens supply chain resilience but also enhances operational efficiency and organizational preparedness in the face of future disruptions.
Who can learn from the Shortage of Medicines template?
- Supply Chain and Logistics Teams: They can understand how factors like transportation disruptions and poor inventory tracking contribute to shortages, helping them optimize distribution strategies.
- Manufacturing and Production Teams: Insights into capacity limitations and quality control issues enable them to improve production planning, facility utilization, and product reliability.
- Regulatory Affairs Teams: By analyzing causes such as lengthy approval processes and import/export restrictions, they can streamline compliance workflows and anticipate regulatory bottlenecks.
- Market and Demand Planning Teams: Understanding sudden demand surges and unpredictable forecasting helps them develop more accurate demand predictions and responsive supply strategies.
- Finance and Operations Departments: They can learn how high production costs and low profit margins affect resource allocation, enabling better budgeting and investment in critical supply areas.
- Human Resources and Workforce Management Teams: By reviewing skilled labor shortages and operational disruptions, they can implement training, retention, and staffing strategies to maintain a resilient workforce.
Why use this template?
GEN-AI powered RCA with ProSolvr transforms medicine shortages into structured learning opportunities. It helps pharmaceutical organizations design and implement effective CAPA, strengthen supply chain reliability, and maintain trust with healthcare providers and patients, ensuring that essential therapies and medications remain available when needed.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to systematically mitigate challenges in the pharmaceutical industry and build long-term operational resilience.