RCA of Security Misconfigurations
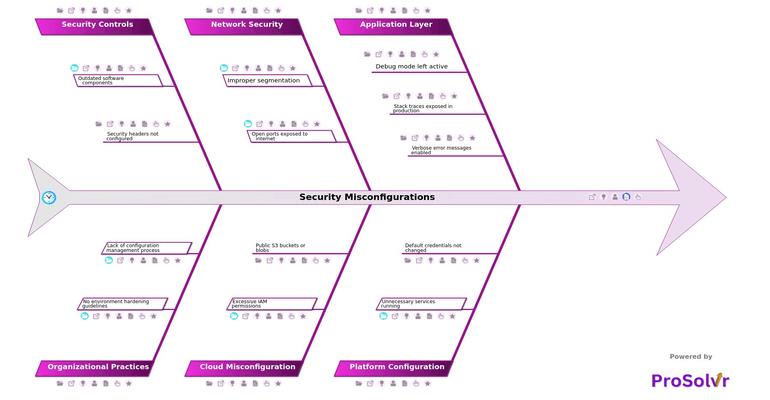
Security misconfiguration is one of the most common problems that weaken cybersecurity. It happens when applications, platforms, networks, or cloud systems are not set up correctly. Simple mistakes like leaving debug mode on, showing stack traces or error messages in production, running unused services, or keeping default passwords can give attackers easy access. Open ports without proper firewall protection also make systems vulnerable and can lead to data leaks or service downtime.
In cloud environments, misconfigurations can cause even bigger issues. Granting excessive IAM permissions or leaving storage buckets public can expose sensitive data to the internet. Using outdated software, missing security headers, and not following environment hardening guidelines increase the risk further. These problems often occur because of poor configuration management, manual changes, or no clear security standards. Over time, they build up and create hidden weaknesses that threaten the whole organization.
When a security incident happens, it is important to understand why it occurred. ProSolvr uses a GenAI-powered Root Cause Analysis (RCA) method based on Six Sigma principles to help teams find the real cause. By showing connections across the application, platform, network, cloud, and organizational levels through visual Fishbone diagrams, ProSolvr helps uncover how small gaps lead to bigger failures.
Through this structured RCA process, ProSolvr turns investigation results into useful insights. It helps teams plan strong Corrective and Preventive Actions, improve configuration management, and reduce future risks. With its visual and collaborative workspace, ProSolvr makes it easier for organizations to solve cybersecurity issues quickly and build lasting resilience.
Who can learn from the Security Misconfigurations template?
- System Administrators: System administrators can use the RCA to identify and correct missteps, which increase the attack surface. Learning from these mistakes helps them implement standardized configuration baselines and tighten system hardening practices.
- DevOps Teams: DevOps teams gain insights into how deployment oversights can compromise security. This understanding encourages the integration of security checks into CI/CD pipelines to prevent recurrence.
- Cloud Engineers: Cloud engineers can learn how various issues can lead to critical vulnerabilities. The RCA helps them apply the principle of least privilege and enforce tighter access control policies in cloud environments.
- Security Analysts: Security analysts benefit from RCA findings by identifying patterns across incidents, without proper firewall rules. This enables them to better tune detection systems and prioritize remediation efforts.
- IT Managers: IT managers can understand how organizational gaps contribute to security failures. This empowers them to drive policy changes and invest in training or automation tools.
- Compliance and Audit Teams: Compliance teams learn how misconfigurations can lead to regulatory risks. RCA outcomes guide them in refining audit checklists and enforcing compliance with industry standards.
Why use this template?
ProSolvr uses AI-driven Root Cause Analysis (RCA) with visual Fishbone diagrams to make the RCA process faster and more structured. By organizing causes under clear categories, ProSolvr helps teams trace problems systematically, prioritize issues, assign actions, and document CAPA measures with ease. The platform encourages continuous improvement and smarter collaboration among cybersecurity teams, helping organizations strengthen their defenses after every incident.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to efficiently resolve security misconfigurations and improve the overall resilience of your organization