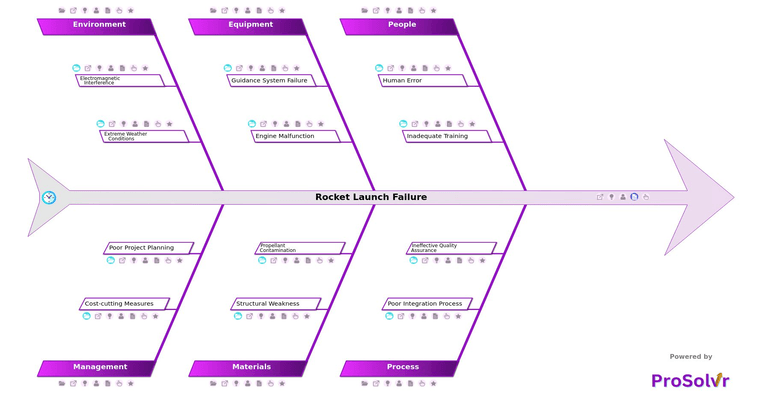
Rocket Launch Failure Root Cause Analysis
A rocket launch failure happens when a rocket cannot reach the path or orbit it was meant to follow during preparation, lift-off, or ascent. These failures can be caused by many factors such as human mistakes, equipment issues, material defects, environmental conditions, or gaps in processes and planning. Because rockets operate under extreme pressure, temperature, and speed, even a small error can lead to major consequences.
The impact of a launch failure can be serious. It can destroy expensive payloads, damage launch infrastructure, delay missions, and weaken confidence among space agencies and investors. Often, the problem is not just one issue but a combination of small defects or errors that come together at the wrong moment.
After a failure, teams conduct a root cause analysis (RCA) to understand what went wrong and how to prevent it in the future. A fishbone diagram is a helpful tool because it groups possible causes into clear categories such as 5M 1E. This structured approach makes it easier to see the bigger picture instead of focusing only on surface-level symptoms.
By organizing information in this way, teams can identify real weaknesses and develop strong corrective and preventive actions. A Gen-AI powered tool like ProSolvr supports this process by helping teams analyze data, highlight probable causes, and guide investigations more effectively. This leads to clearer decisions, faster learning, and improved reliability in future launches.
Who can learn from the Rocket Launch Failure template?
- Aerospace Engineers: They can learn how design flaws, equipment failures, and material issues contribute to launch failures, helping them strengthen engineering practices and system reliability.
- Quality Assurance and Testing Teams: These teams can use the RCA insights to understand gaps in inspections, testing protocols, and integration processes, enabling them to enhance quality controls and validation procedures.
- Launch Operations and Ground Crew: They can benefit from understanding human errors and procedural lapses, such as failures in pre-launch checklists, improving operational discipline and adherence to protocols.
- Project and Program Managers: RCA outcomes help managers understand how planning issues, resource constraints, and cost-cutting measures impact mission safety and success, supporting better decision-making and risk management.
- Training and Skill Development Teams: These groups can learn from training-related causes such as inadequate simulations or lack of experience with new propulsion systems, helping them develop more effective competency programs.
- Safety and Risk Management Teams: By reviewing the causes and systemic weaknesses, they can enhance safety frameworks, refine hazard assessments, and reinforce preventive strategies across the aerospace lifecycle.
Why use this template?
ProSolvr helps aerospace teams understand what caused a launch failure and what actions are needed to prevent it from happening again. Launch failures can happen during preparation, lift off, or ascent, and they often result from small problems that add up. ProSolvr makes it easier to find the real causes, organize the facts, and create clear Corrective and Preventive Actions that teams can follow. This helps avoid repeat issues, protects important missions, and improves the reliability of every future launch.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to systematically reduce errors and eliminate issues that can prevent rocket launch failures, saving billions of dollars in the process.
Curated from community experience and public sources: