Root Cause Analysis of Recurring Service Issues
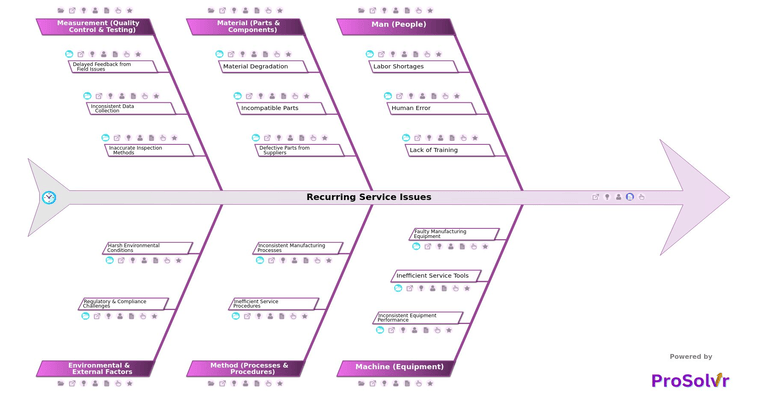
Recurring service issues are a major challenge in the automotive industry, leading to costly repairs, warranty claims, and customer dissatisfaction. These problems often stem from labor shortages, high employee turnover, and rushed repairs, which increase the likelihood of human errors such as misdiagnosis of vehicle issues, poor adherence to service manuals, and incorrect installation of parts. Additionally, as vehicles become more technologically advanced, a lack of up-to-date knowledge on new automotive systems further contributes to recurring failures. Without a structured approach to identifying and preventing these root causes, manufacturers and service centers struggle to maintain consistent quality and efficiency.
Equipment-related failures also play a critical role in recurring service issues. Inconsistent torque application on fasteners, sensor malfunctions in production lines, and variability in welding, painting, or assembly processes all contribute to defects that resurface in multiple vehicles. Furthermore, inefficient service tools, calibration issues, and outdated diagnostic equipment lead to incorrect repairs, compounding the problem. On the material side, rapid wear and tear of electrical components, corrosion of metal parts, and software-hardware integration issues create ongoing service challenges that require repeated interventions, increasing costs and downtime.
To prevent these recurring failures, automotive manufacturers and service providers need a structured visual Root Cause Analysis (RCA) application powered by Gen AI. Traditional troubleshooting methods often focus on short-term fixes rather than addressing underlying problems. ProSolvr enables teams to systematically analyze failures using Fishbone Diagrams, breaking them down into key factors like people, machines, materials, processes, and quality control. This approach helps identify inefficiencies, such as non-standardized diagnostic workflows, unstructured service protocols, and poor supplier quality control, allowing organizations to develop targeted Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) to eliminate recurring issues at their source.
By adopting ProSolvr’s structured problem-solving approach, manufacturers can reduce quality inconsistencies, warranty claims, and operational inefficiencies, while improving service reliability. With CAPA-driven solutions, organizations can prevent repeated failures, ensuring higher vehicle quality, lower maintenance costs, and improved customer trust. In an industry where precision and consistency are critical, leveraging Gen AI-powered RCA ensures that service issues don’t just get fixed—they get permanently resolved.
Who can use the Recurring Service Issues template?
- Automobile Manufacturers: Engineers and production managers can use RCA to improve vehicle designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control, reducing recurring failures and enhancing product reliability.
- Automobile Service Technicians and Mechanics: Technicians can apply RCA to improve diagnostic skills, avoid common mistakes, and follow standardized repair procedures to reduce service issues.
- Quality Assurance and Control Teams: QA and QC teams can refine testing procedures, identify production weak points, and implement proactive measures to prevent defects and recurring issues.
- Supply Chain Managers: Supply chain managers can analyze RCA to improve supplier quality control, streamline procurement, and prevent material-related problems from affecting product quality.
- Training and Development Managers: HR and training managers can identify gaps in skills or knowledge and create better training programs to reduce errors and improve employee performance.
- Regulatory and Compliance Officers: Compliance officers can use RCA to understand the impact of regulatory changes and ensure the company stays compliant, minimizing service failures linked to non-compliance.
Why use this template?
An application like ProSolvr, which use fishbone diagrams powered by GEN-AI, provide a structured yet dynamic approach to problem-solving. It can analyze complex problems by categorizing potential causes and guiding users through a logical progression of inquiries based on Six Sigma principles. Using such AI-powered root cause analysis applications helps automate the analysis of complex issues and ensures consistency across problem-solving processes. By systematically addressing underlying causes and continuously updating corrective, preventive, and investigative actions (CAPA), organizations can implement lasting solutions for their automobile plants.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for efficient problem-solving in your organization.