RCA of Uncontrolled Gas Releases
Uncontrolled gas releases in petrochemical plants are critical incidents involving the unintentional discharge of flammable or toxic gases into the environment. These events can be triggered by several factors, including equipment malfunctions, inadequate maintenance, operator errors, or external factors like corrosion or weather conditions. A structured fishbone analysis (Ishikawa diagram) is an invaluable tool for identifying and mitigating the root causes of these incidents.
The repercussions of uncontrolled gas releases are severe, with potential for catastrophic events like explosions, fires, and environmental contamination. Beyond the immediate physical dangers, these incidents pose significant operational and reputational risks, including regulatory fines and loss of public trust. Despite robust detection systems and strict adherence to safety protocols, these releases remain a persistent challenge, underscoring the necessity of root cause analysis to not only address the current issues but also implement sustainable preventative measures.
Applying Six Sigma principles within this RCA framework allows for a systematic approach to categorizing potential causes— whether stemming from mechanical, procedural, or human factors. By thoroughly mapping these relationships, plants can identify latent defects or gaps, such as improper calibration of safety valves or inadequate staff training. For instance, an equipment failure may highlight systemic issues in the preventive maintenance schedule, while operational errors could reveal deficiencies in the plant’s safety culture or communication processes.
Ultimately, leveraging RCA through tools like fishbone diagrams enables petrochemical plants to pinpoint precise failure modes, enhance safety protocols, and significantly reduce the likelihood of future gas releases. This proactive, data-driven approach fosters a more resilient operational environment.
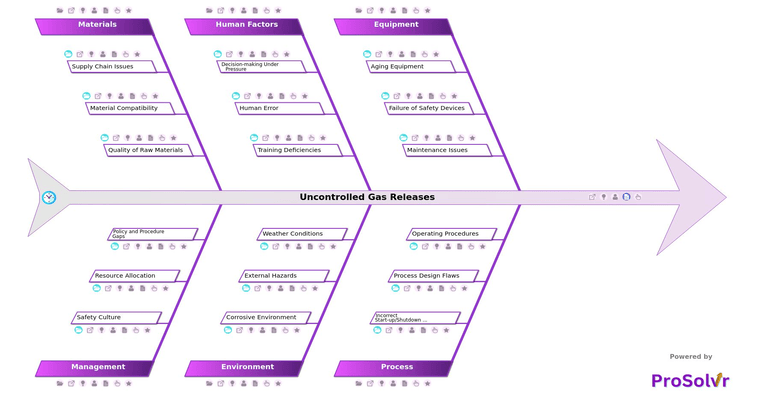
Root Causes of Uncontrolled Gas Releases
- Uncontrolled Gas Releases
- Equipment
- Aging Equipment
- Wear and tear in seals and gaskets
- Corrosion in pipes and valves
- Failure of Safety Devices
- Gas detectors failing
- Pressure relief valves malfunctioning
- Maintenance Issues
- Use of improper tools
- Inadequate maintenance schedule
- Aging Equipment
- Process
- Incorrect Start-up/Shutdown Procedures
- Insufficient cool-down periods
- Errors during plant start-up
- Process Design Flaws
- Poorly designed pressure control systems
- Inadequate fail-safes in the system
- Operating Procedures
- Lack of monitoring during critical operations
- Deviations from SOPs
- Incorrect Start-up/Shutdown Procedures
- Human Factors
- Decision-making Under Pressure
- Lack of clarity in roles and responsibilities
- Rushed decisions during emergencies
- Human Error
- Miscommunication during shift handovers
- Operator fatigue leading to mistakes
- Training Deficiencies
- Lack of regular drills and simulations
- Insufficient training on emergency procedures
- Decision-making Under Pressure
- Environment
- Corrosive Environment
- High humidity accelerating equipment degradation
- Presence of corrosive chemicals in the atmosphere
- External Hazards
- Natural disasters impacting plant stability
- Nearby construction causing vibrations or damage
- Weather Conditions
- High winds disrupting gas flow or dispersal
- Extreme temperatures affecting equipment integrity
- Corrosive Environment
- Materials
- Supply Chain Issues
- Poor quality control from suppliers
- Delays in receiving critical replacement parts
- Material Compatibility
- Use of substandard materials in construction
- Incompatible materials causing corrosion
- Quality of Raw Materials
- Contaminated feedstock leading to process upsets
- Impurities in gases causing unexpected reactions
- Supply Chain Issues
- Management
- Safety Culture
- Lack of enforcement of safety regulations
- Complacency towards safety protocols
- Resource Allocation
- Understaffing in critical areas
- Insufficient budget for maintenance and upgrades
- Policy and Procedure Gaps
- Inadequate incident investigation and follow-up
- Lack of a robust risk management framework
- Safety Culture
- Equipment
Suggested Actions Checklist
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of uncontrolled gas releases in petrochemical plants can provide valuable insights for various industry experts.
- Equipment
- Aging Equipment
- Wear and Tear in Seals and Gaskets
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace worn seals and gaskets immediately.
- Apply temporary fixes if immediate replacement is not feasible, with a plan for prompt follow-up.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a regular inspection and replacement schedule for seals and gaskets.
- Use high-quality materials designed to withstand the specific operating conditions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze failure modes of seals and gaskets to determine root causes of wear.
- Investigate whether material selection and environmental factors contributed to the degradation.
- Corrosion in Pipes and Valves
- Corrective Actions:
- Remove and replace corroded sections of pipes and valves.
- Apply corrosion inhibitors and protective coatings where feasible.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly inspect piping and valves for early signs of corrosion.
- Use corrosion-resistant materials and coatings in high-risk areas.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the sources and mechanisms of corrosion.
- Review the effectiveness of current corrosion prevention measures.
- Wear and Tear in Seals and Gaskets
- Failure of Safety Devices
- Gas Detectors Failing
- Corrective Actions:
- Immediately repair or replace malfunctioning gas detectors.
- Calibrate and test all detectors to ensure proper functionality.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a regular testing and maintenance schedule for gas detectors.
- Install redundant systems to detect failures.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the reasons for detector failures, such as environmental factors or maintenance lapses.
- Review the detector placement and calibration protocols.
- Pressure Relief Valves Malfunctioning
- Corrective Actions:
- Repair or replace faulty pressure relief valves.
- Adjust settings and ensure proper calibration.
- Preventive Actions:
- Conduct regular maintenance and testing of pressure relief valves.
- Implement a redundant system for critical relief valves.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the causes of valve malfunction, such as material degradation or improper settings.
- Review the maintenance history and calibration records.
- Gas Detectors Failing
- Maintenance Issues
- Use of Improper Tools
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace improperly used tools and recheck affected components.
- Retrain maintenance personnel on proper tool usage.
- Preventive Actions:
- Provide the correct tools for all maintenance tasks and ensure they are readily available.
- Implement a tool control and training program to prevent misuse.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the incidents of improper tool usage and their impact on equipment integrity.
- Review training records and assess gaps in knowledge or supervision.
- Inadequate Maintenance Schedule
- Corrective Actions:
- Revise and implement a more comprehensive maintenance schedule immediately.
- Prioritize overdue maintenance tasks.
- Preventive Actions:
- Establish a proactive maintenance program with a focus on high-risk areas.
- Use predictive maintenance techniques to optimize schedules.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the adequacy of the current maintenance schedule and identify areas for improvement.
- Review past maintenance records to determine patterns of neglect or oversight.
- Use of Improper Tools
- Aging Equipment
- Process
- Incorrect Start-up/Shutdown Procedures
- Insufficient cool-down periods
- Corrective Actions:
- Adjust procedures to include adequate cool-down periods.
- Train operators on the importance of cool-down times and their impact on safety.
- Preventive Actions:
- Review and standardize start-up/shutdown procedures to ensure consistency.
- Implement automatic controls to manage cool-down periods.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate incidents where insufficient cool-down contributed to equipment stress or failure.
- Review procedural documents to identify gaps or inconsistencies.
- Errors during plant start-up
- Corrective Actions:
- Address the immediate impact of start-up errors, such as releasing excess pressure or correcting temperature imbalances.
- Retrain staff on correct start-up procedures.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a checklist and monitoring system for start-up operations.
- Conduct regular simulations and drills to reinforce correct procedures.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the root causes of start-up errors, such as insufficient training or unclear procedures.
- Analyze start-up procedures for potential failure points.
- Insufficient cool-down periods
- Process Design Flaws
- Poorly designed pressure control systems
- Corrective Actions:
- Modify or replace inadequate pressure control systems.
- Conduct a thorough review of the pressure control strategy and implement necessary changes.
- Preventive Actions:
- Ensure new designs undergo rigorous testing and validation.
- Involve experienced engineers in the design and review process.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the design process to identify why flaws were not detected earlier.
- Review system performance data to assess the impact of design flaws.
- Inadequate fail-safes in the system
- Corrective Actions:
- Install or upgrade fail-safe systems where needed.
- Test and validate existing fail-safes to ensure reliability.
- Preventive Actions:
- Design systems with multiple layers of fail-safes.
- Regularly review and update fail-safe mechanisms as part of the process safety management program.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate incidents where fail-safes failed or were bypassed.
- Review the overall system design to identify weaknesses in fail-safe implementation.
- Poorly designed pressure control systems
- Operating Procedures
- Lack of monitoring during critical operations
- Corrective Actions:
- Increase monitoring during critical operations, using both automated systems and human oversight.
- Address any immediate operational issues that were missed due to lack of monitoring.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement real-time monitoring systems with alarms and automatic shutdown features.
- Train operators on the importance of monitoring and the use of monitoring tools.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate why monitoring was insufficient and its impact on the operation.
- Review past incidents to identify patterns of inadequate monitoring.
- Deviations from SOPs
- Corrective Actions:
- Reinforce adherence to SOPs through training and supervision.
- Address any specific incidents of SOP deviation and correct the process.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly review and update SOPs to ensure they are clear, relevant, and practical.
- Implement checks and audits to ensure compliance with SOPs.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the causes of SOP deviations, including human factors and procedural clarity.
- Review the effectiveness of SOP training programs.
- Lack of monitoring during critical operations
- Incorrect Start-up/Shutdown Procedures
- Human Factors
- Decision-making Under Pressure
- Lack of clarity in roles and responsibilities
- Corrective Actions:
- Clarify roles and responsibilities during emergencies through updated procedures.
- Conduct immediate drills to reinforce these roles.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement clear, well-communicated emergency response plans.
- Regularly train and assess staff on their roles during high-pressure situations.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate incidents of unclear roles leading to poor decisions.
- Review the emergency response plan for clarity and effectiveness.
- Rushed decisions during emergencies
- Corrective Actions:
- Address the consequences of rushed decisions and stabilize operations.
- Retrain staff on decision-making under pressure with a focus on following protocols.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement decision support systems and tools to assist during emergencies.
- Train staff on situational awareness and the importance of following procedures even under pressure.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past emergency responses to identify why rushed decisions were made.
- Review training programs to ensure they adequately prepare staff for emergency situations.
- Lack of clarity in roles and responsibilities
- Human Error
- Miscommunication during shift handovers
- Corrective Actions:
- Immediately clarify any miscommunications and correct ongoing operations.
- Implement a formalized handover protocol to ensure clear communication.
- Preventive Actions:
- Introduce standardized shift handover checklists and logs.
- Train staff on effective communication techniques during handovers.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past miscommunications to determine root causes.
- Review and improve the handover process to prevent future issues.
- Operator fatigue leading to mistakes
- Corrective Actions:
- Provide immediate relief to fatigued operators and review their tasks.
- Adjust work schedules to prevent further fatigue.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement fatigue management programs, including sufficient rest periods and workload management.
- Regularly assess operator alertness and well-being.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate work schedules and workloads to identify causes of fatigue.
- Review the impact of fatigue on past incidents and adjust operational practices accordingly.
- Miscommunication during shift handovers
- Training Deficiencies
- Lack of regular drills and simulations
- Corrective Actions:
- Schedule and conduct emergency drills and simulations immediately.
- Review and update training materials based on the outcomes of these drills.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a regular schedule of drills and simulations covering a range of scenarios.
- Evaluate and improve training programs continuously based on drill outcomes.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate why drills and simulations were not conducted regularly.
- Review the training program to identify and address any deficiencies.
- Insufficient training on emergency procedures
- Corrective Actions:
- Provide targeted training on emergency procedures immediately.
- Assess operator competence and understanding following the training.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop comprehensive emergency procedure training programs with regular refreshers.
- Implement certifications or assessments to ensure proficiency in emergency procedures.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past emergency responses to determine the impact of training deficiencies.
- Review and enhance the emergency training curriculum.
- Lack of regular drills and simulations
- Decision-making Under Pressure
- Environment
- Corrosive Environment
- High humidity accelerating equipment degradation
- Corrective Actions:
- Apply anti-corrosion treatments and address immediate damage.
- Improve ventilation or dehumidification systems to control humidity levels.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly inspect for corrosion and environmental conditions in high-humidity areas.
- Use corrosion-resistant materials in areas prone to high humidity.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the correlation between humidity levels and equipment degradation.
- Review the effectiveness of current environmental controls.
- Presence of corrosive chemicals in the atmosphere
- Corrective Actions:
- Neutralize or control the release of corrosive chemicals in the atmosphere.
- Replace or repair affected equipment immediately.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement air quality monitoring systems to detect corrosive chemicals.
- Use protective coatings and materials resistant to the identified chemicals.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate sources of corrosive chemicals and their impact on plant equipment.
- Review the environmental control measures and their effectiveness.
- High humidity accelerating equipment degradation
- External Hazards
- Natural disasters impacting plant stability
- Corrective Actions:
- Conduct a damage assessment and take immediate stabilization actions.
- Implement emergency protocols to manage the impact of natural disasters.
- Preventive Actions:
- Design and retrofit facilities to withstand local natural disaster risks.
- Develop and regularly update emergency response plans specific to natural disasters.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate how natural disasters have affected plant stability in the past.
- Review and update risk assessments related to external hazards.
- Nearby construction causing vibrations or damage
- Corrective Actions:
- Assess and repair any damage caused by external vibrations.
- Coordinate with nearby construction projects to minimize impact.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement vibration monitoring systems to detect external influences.
- Design facilities to mitigate the impact of external vibrations.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past incidents where external construction contributed to equipment failures.
- Review and update the plant’s risk management strategies for external hazards.
- Natural disasters impacting plant stability
- Weather Conditions
- High winds disrupting gas flow or dispersal
- Corrective Actions:
- Implement immediate measures to stabilize gas flow, such as wind barriers.
- Adjust operations to minimize the impact of wind conditions.
- Preventive Actions:
- Install protective structures or modify plant layout to reduce wind impact.
- Implement weather monitoring systems to anticipate and respond to high wind conditions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the effects of wind on gas flow and dispersal.
- Review the design and operational procedures for resilience to weather conditions.
- Extreme temperatures affecting equipment integrity
- Corrective Actions:
- Implement cooling or heating measures to stabilize affected equipment.
- Replace or reinforce components damaged by extreme temperatures.
- Preventive Actions:
- Design equipment to withstand the range of expected temperatures.
- Monitor environmental conditions and adjust operations accordingly.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate incidents where extreme temperatures impacted equipment performance.
- Review the adequacy of existing temperature control systems.
- High winds disrupting gas flow or dispersal
- Corrosive Environment
- Materials
- Supply Chain Issues
- Poor quality control from suppliers
- Corrective Actions:
- Inspect and replace any substandard materials or components immediately.
- Notify suppliers of the quality issues and seek remediation or alternatives.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a rigorous supplier vetting and quality assurance program.
- Establish long-term relationships with reliable suppliers.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the root causes of quality issues in the supply chain.
- Review supplier performance and quality control processes.
- Delays in receiving critical replacement parts
- Corrective Actions:
- Expedite procurement and install temporary solutions if possible.
- Adjust maintenance schedules to account for part delays.
- Preventive Actions:
- Establish buffer stocks of critical parts to avoid delays.
- Work with multiple suppliers to ensure redundancy in the supply chain.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the causes of delays and their impact on plant operations.
- Review the supply chain management strategy to improve reliability.
- Poor quality control from suppliers
- Material Compatibility
- Use of substandard materials in construction
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace substandard materials with appropriate ones.
- Conduct an audit of all materials used in critical areas.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement strict material specifications and quality checks during procurement.
- Ensure materials are selected based on their compatibility with operational conditions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate how substandard materials were selected and approved for use.
- Review the material selection process and make necessary improvements.
- Incompatible materials causing corrosion
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace incompatible materials with corrosion-resistant alternatives.
- Address and repair any damage caused by corrosion.
- Preventive Actions:
- Conduct compatibility testing before selecting materials for use in construction.
- Use coatings and barriers to protect materials from corrosive interactions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the corrosion mechanisms and material interactions.
- Review material selection criteria and compatibility testing procedures.
- Use of substandard materials in construction
- Quality of Raw Materials
- Contaminated feedstock leading to process upsets
- Corrective Actions:
- Purge and replace contaminated feedstock to stabilize the process.
- Inspect and clean affected equipment if necessary.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement strict quality control measures for incoming raw materials.
- Work closely with suppliers to ensure the purity of feedstock.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the sources and impacts of feedstock contamination.
- Review and improve raw material testing procedures.
- Impurities in gases causing unexpected reactions
- Corrective Actions:
- Isolate and neutralize affected gases.
- Adjust the process to minimize the impact of impurities.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement gas purity testing and monitoring systems.
- Specify strict purity requirements for all gas supplies.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the sources and effects of gas impurities.
- Review and strengthen supplier agreements and quality controls.
- Contaminated feedstock leading to process upsets
- Supply Chain Issues
- Management
- Safety Culture
- Lack of enforcement of safety regulations
- Corrective Actions:
- Enforce safety regulations rigorously and address non-compliance immediately.
- Review and revise safety policies to ensure they are practical and enforceable.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a strong safety culture through regular training and leadership involvement.
- Conduct regular safety audits and enforce accountability.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the reasons for lapses in safety enforcement.
- Review and improve the safety management system.
- Complacency towards safety protocols
- Corrective Actions:
- Reinforce the importance of safety protocols through training and communication.
- Address incidents of complacency with appropriate disciplinary actions.
- Preventive Actions:
- Promote a safety-first mindset at all levels of the organization.
- Implement continuous improvement programs focused on safety awareness.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate incidents where complacency contributed to safety violations.
- Review the effectiveness of safety communications and training.
- Lack of enforcement of safety regulations
- Resource Allocation
- Understaffing in critical areas
- Corrective Actions:
- Hire additional staff or redistribute workload to ensure critical areas are adequately staffed.
- Provide immediate support to understaffed areas to manage current risks.
- Preventive Actions:
- Conduct regular staffing assessments to ensure adequate coverage in all critical areas.
- Develop contingency plans to address sudden staffing shortages.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the impact of understaffing on plant operations and safety.
- Review resource allocation and budgeting practices.
- Insufficient budget for maintenance and upgrades
- Corrective Actions:
- Reallocate funds to prioritize critical maintenance and upgrades.
- Address immediate maintenance needs through temporary fixes if necessary.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop a long-term budget plan that prioritizes maintenance and upgrades.
- Advocate for increased investment in plant safety and reliability.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate the budget allocation process to identify shortfalls.
- Review the impact of budget constraints on equipment reliability and safety.
- Understaffing in critical areas
- Policy and Procedure Gaps
- Inadequate incident investigation and follow-up
- Corrective Actions:
- Conduct thorough investigations of recent incidents and implement corrective actions.
- Improve documentation and tracking of incidents and corrective actions.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop a robust incident investigation procedure with clear follow-up protocols.
- Train staff on incident reporting and investigation techniques.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past incidents to determine why investigations were inadequate.
- Review and improve incident investigation procedures.
- Lack of a robust risk management framework
- Corrective Actions:
- Develop and implement a comprehensive risk management framework.
- Conduct a risk assessment of current operations and address identified risks.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly review and update the risk management framework to address emerging risks.
- Train staff on risk management principles and procedures.
- Investigative Actions:
- Investigate past incidents and near-misses to identify gaps in risk management.
- Review and benchmark the risk management practices against industry standards.
- Inadequate incident investigation and follow-up
- Safety Culture
Who can learn from the Uncontrolled Gas Releases template?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of Uncontrolled Gas Releases provide valuable insights for various stakeholder
- Process Safety Engineers: To identify and mitigate potential hazards in petrochemical processes, ensuring safer plant operations.
- Maintenance Teams: To understand equipment-related risks, such as aging components and maintenance issues, and implement preventive measures.
- Operations Managers: To oversee the correct implementation of start-up/shutdown procedures and ensure adherence to operating standards.
- Training Coordinators: To design and conduct training programs that address human factors like decision-making under pressure and emergency procedures.
- Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) Professionals: To assess and manage the environmental factors and external hazards that could contribute to gas releases.
- Quality Assurance and Supply Chain Managers: To ensure the quality and compatibility of materials and manage supply chain risks that might impact plant safety.
Why use this template?
Using Gen-AI powered root cause analysis for the uncontrolled gas releases template is crucial for systematically identifying the underlying causes of such hazardous incidents. RCA helps organizations move beyond merely addressing the symptoms of a problem by uncovering the fundamental issues—whether related to equipment, processes, human factors, or management practices. By understanding these root causes, petrochemical plants can implement targeted corrective actions, enhance safety protocols, and prevent future occurrences of uncontrolled gas releases. This proactive approach not only safeguards human lives and the environment but also ensures regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.