RCA of Raw Material Quality Failures
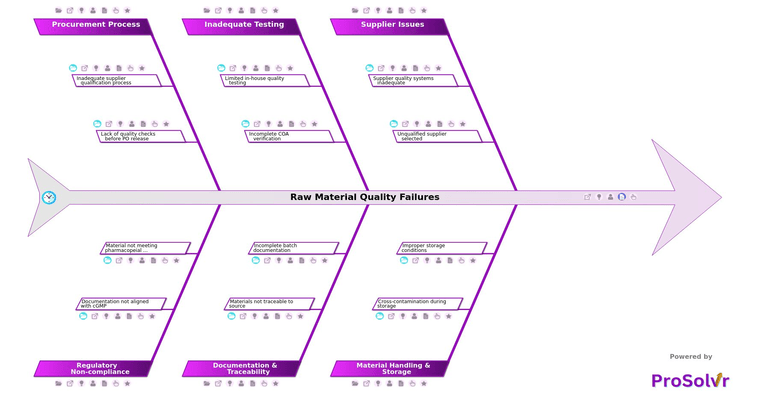
Raw material quality failures in the pharmaceutical industry often stem from a combination of supplier issues, poor storage practices, and weak internal controls. Unqualified suppliers, especially those not audited or lacking CAPA implementation for past issues, pose a high risk to raw material integrity. When procurement processes do not include quality checks before purchase order release or rely solely on cost-based decisions, the likelihood of introducing non-compliant ingredients into the production line increases significantly.
Material handling and storage deficiencies are another major cause. Cross-contamination during storage—particularly in shared spaces with incompatible materials—can compromise batch quality. Improper storage conditions such as humidity or temperature excursions further degrade raw materials. In many cases, limited in-house testing and over-reliance on third-party results mean that quality deviations go undetected. Incomplete COA verification and test results not cross-checked against USP, EP, or JP specifications weaken compliance and quality assurance.
Effective resolution of such failures requires a structured and thorough Root Cause Analysis. ProSolvr enables quality teams to visually explore interconnected causes using Six Sigma-based fishbone diagrams. Its collaborative interface helps teams uncover root contributors like incomplete batch documentation, missing sampling logs, or unverified material traceability. This structured, layered approach moves teams from guesswork to evidence-backed conclusions, making CAPA more focused and effective.
By addressing core issues such as inadequate supplier qualification, insufficient COA checks, and documentation not aligned with cGMP, pharmaceutical companies can prevent recurring material failures. ProSolvr helps transform complex problem-solving into a visual, team-driven process that supports compliance, audit readiness, and continuous improvement. This approach not only reduces risk but also strengthens operational reliability and product safety across the value chain.
Who can learn from the Raw Materials Quality Failures template?
- Quality Assurance (QA) Teams: QA teams can use the findings from the RCA to strengthen their internal quality controls and improve compliance monitoring practices. It enables them to better align procedures with regulatory expectations and prevent future lapses.
- Regulatory Affairs Professionals: By analyzing where documentation or compliance issues occurred, regulatory professionals can refine their processes to ensure readiness for audits and inspections. It also helps in preparing more robust responses to regulatory authorities.
- Procurement and Vendor Management Teams: These teams can use the RCA insights to enhance supplier selection, auditing, and evaluation practices. It reinforces the importance of quality over cost and builds a more reliable supplier base.
- Manufacturing and Operations Managers: The RCA helps operations teams identify where procedural breakdowns have occurred and adjust workflows accordingly. This supports more consistent production outcomes and reduces operational risks.
- Research and Development (R&D) Teams: R&D can learn how upstream material or process flaws impact product performance and quality. This understanding can guide better material specifications and process design during development.
- Training and Human Resources (HR) Departments: Training teams can use the RCA to identify skill gaps and target training interventions more effectively. HR can integrate these insights into competency development and performance assessments.
Why use this template?
Applications like ProSolvr, which incorporate GEN-AI to build and analyze fishbone diagrams, significantly elevate the efficacy of root cause analysis. By allowing users to map various causes into an interactive, visual diagram, ProSolvr facilitates clearer understanding and communication among cross-functional teams. Once the root causes are identified, the platform can assist organizations in generating structured CAPA plans tied directly to those causes, ensuring that actions are strategically preventive.
ProSolvr's strength lies in its ability to provide a guided analytical path. Pharmaceutical companies can use ProSolvr to ensure continuous improvement throughout the organization.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effectively rooting out problems in your organization.