RCA of Oil and Gas Separator Issues
Oil and gas separators play a crucial role in petrochemical plants by separating the mixture of oil, gas, and water extracted from wells. Common causes of oil and gas separator issues include improper design, inadequate maintenance, faulty instrumentation, and human error. These problems can result in unplanned downtime, loss of production, and increased operational costs. Poor separation can cause damage to downstream equipment, such as compressors and pipelines, due to the presence of contaminants like water or gas in the oil stream.
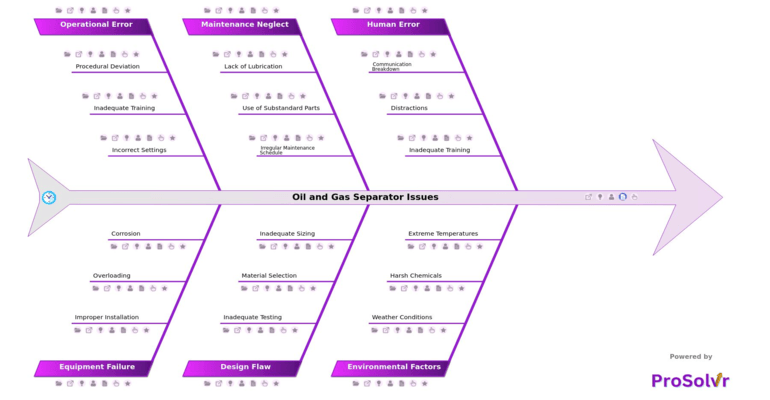
When these separators malfunction, it can lead to several significant issues, including reduced efficiency in separating the components, contamination of the separated products, and even complete shutdowns of the plant. For example, communication breakdowns or distractions during operations can result in human errors, while harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures can intensify wear and tear on separator components. Neglecting regular maintenance, using substandard parts, or inadequate testing during the design phase can further compound these problems, causing unplanned downtime, product loss, and even safety hazards.
Root cause analysis (RCA) is an essential tool for addressing oil and gas separator issues in petrochemical plants, as it systematically identifies and addresses underlying causes to prevent recurrence. For instance, human error, such as communication breakdowns or distractions, can lead to procedural deviations and incorrect settings during operations, directly impacting separator performance. Environmental factors, including weather conditions, exposure to harsh chemicals, and extreme temperatures, can degrade equipment, resulting in corrosion or other failures.
Maintenance neglect, such as lack of lubrication, use of substandard parts, or an irregular maintenance schedule, often aggravates equipment problems, leading to improper installation or overloading. Additionally, design flaws, such as inadequate testing, poor material selection, or improper sizing, can create long-term operational challenges. By thoroughly investigating these issues through RCA, petrochemical plants can implement corrective actions like enhanced training programs, robust maintenance schedules, and improved design standards, ensuring reliable separator operation and minimizing downtime.
Root cause analysis with ProSolvr can provide a systematic approach to identify and address the underlying causes of oil and gas separator issues in petrochemical plants. By thoroughly investigating the problem, RCA can uncover hidden factors contributing to the malfunction, such as design flaws, material defects, or procedural inadequacies. Once the root causes are identified, corrective and preventive actions can be implemented to prevent recurrence, such as redesigning the separator, improving maintenance practices, updating procedures, or providing additional training to operators.
A visual RCA tool like ProSolvr can also help improve the reliability and safety of the plant, reducing the likelihood of future incidents and minimizing the impact on production. An application like ProSolvr, which employs fishbone diagrams for root cause analysis, can further enhance problem-solving efforts. ProSolvr allows users to systematically populate potential causes under predefined categories. ProSolvr not only facilitates detailed analysis but also empowers teams to implement effective solutions, ultimately ensuring smoother operations in petrochemical plants.
Who can learn from the Oil and Gas Separator Issues template?
- Operations Team: Prevent operational errors by learning from common issues and improving daily processes.
- Maintenance Personnel: Adhere to proper schedules, use high-quality parts, and perform thorough inspections to avoid future problems.
- Design Engineers: Gain insights for better design practices, including material selection, sizing, and testing procedures.
- Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Professionals: Use RCA findings to improve safety protocols and training.
- Management: Use RCA to allocate resources effectively and implement policy changes for improved plant performance.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Develop robust quality control measures by understanding potential design, maintenance, and operational issues.
Why use this template?
A root cause analysis with ProSolvr for oil and gas separator issues provides a structured approach to identifying and addressing the underlying causes of problems within the separation process. By systematically examining the various factors, the template helps teams uncover the root causes of failures or inefficiencies. This, in turn, enables the implementation of targeted corrective and preventive actions, ultimately improving the reliability, safety, and efficiency of operations. Additionally, the ProSolvr RCA template facilitates knowledge sharing across teams, promoting continuous improvement and reducing the likelihood of future incidents.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to identify problems with equipment in your plant and prevent future maintenance issues.