RCA of IoT Device Vulnerability
IoT (Internet of Things) device vulnerabilities are a significant cybersecurity concern as more organizations are adopting IoT to streamline operations. These devices, which can include anything from smart thermostats to complex industrial sensors, are often connected to critical infrastructure, making them an attractive target for cyber attackers.
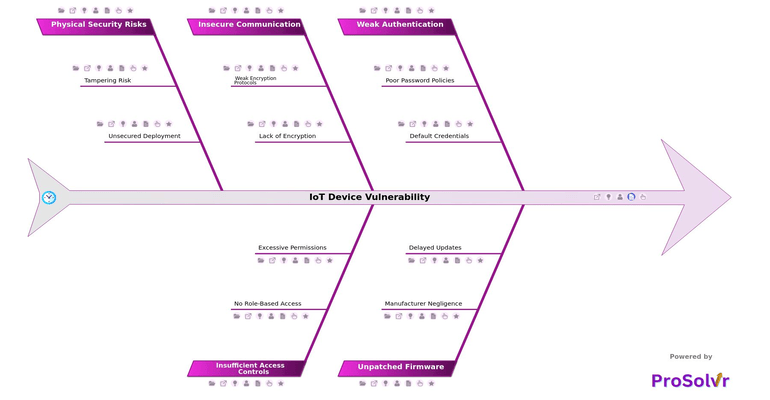
The vulnerabilities often stem from factors such as weak authentication protocols, inadequate encryption standards, and outdated software, which make it easier for hackers to infiltrate networks and manipulate device functions. This can lead to data breaches, operational disruptions, and even physical damage in industries relying heavily on IoT for automation and monitoring, such as manufacturing and energy.
A root cause analysis (RCA) can be crucial for addressing IoT vulnerabilities because it enables organizations to identify and eliminate the underlying causes of cybersecurity risks rather than merely treating symptoms. By employing a structured approach, organizations can delve into factors contributing to vulnerabilities. For example, RCA may reveal that devices were not updated to the latest firmware, or that default passwords were not changed, which are common gaps in IoT security practices.
Conducting an RCA with a Gen-AI powered application like ProSolvr allows IT teams to pinpoint specific failures in processes, device management policies, or user practices, offering a comprehensive view of security lapses that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Who can learn from the IoT Device Vulnerability template?
- IT Security Teams: These professionals are at the forefront of protecting an organization's networks and devices. Through RCA findings, they can identify weak points in IoT security, develop targeted responses, and enhance preventive measures, such as improving patching schedules, monitoring protocols, and device management policies.
- Network Administrators: Since IoT devices operate within organizational networks, network administrators can leverage RCA insights to better understand potential network vulnerabilities caused by IoT devices. They can adjust network segmentation, improve access controls, and ensure robust monitoring to detect anomalies more effectively.
- Operations and Facility Managers: Many IoT vulnerabilities are tied to devices used in facility operations, like smart HVAC systems or security cameras. Facility managers can use RCA findings to enhance physical security protocols, ensure timely updates to critical devices, and adopt a proactive stance in monitoring device health.
- Product Development Teams: RCA insights on IoT vulnerabilities can be invaluable to engineers and designers developing IoT products. This knowledge helps them improve device security features, design with secure firmware update mechanisms, and build more resilient products that can withstand cyber threats from the ground up.
- Senior Management and Compliance Officers: For leadership and compliance teams, understanding IoT vulnerabilities through RCA is essential for informed decision-making, risk management, and regulatory compliance. They can use this knowledge to allocate resources for security initiatives, develop IoT usage policies, and ensure compliance with industry standards on cybersecurity.
Why use this template?
Using a fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagram, helps visualize the different factors contributing to IoT security issues. By organizing the causes under various categories, the fishbone diagram organizes potential root causes in a clear structure, helping teams systematically analyze each component. By using a structured approach with a quality tool and application like ProSolvr, organizations can develop corrective actions and preventive measures that address both technical and procedural aspects, ultimately improving the overall security of IoT implementations.
Strengthen your company’s IoT security today by implementing root cause analysis with ProSolvr by smartQED to identify and resolve vulnerabilities at the source.