RCA of High Off-Gas Production
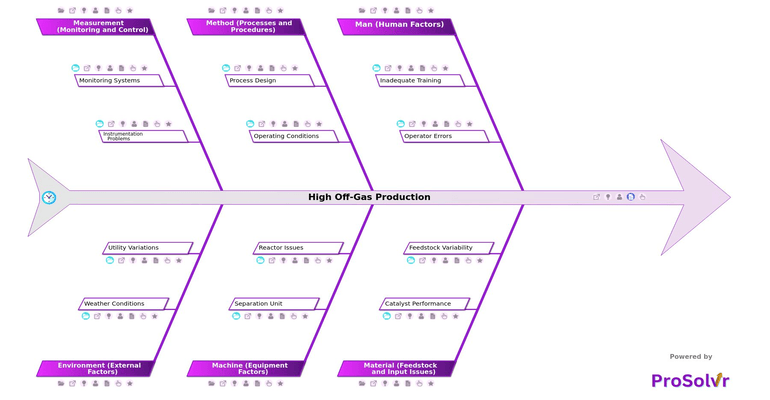
High off-gas production in petrochemical plants, caused by issues like inadequate separation, unstable reactions, and equipment inefficiencies, significantly impacts operational efficiency and profitability. Challenges stem from various factors, including Man (Human Factors) like inadequate training, poor troubleshooting skills, and operator errors, which result in incorrect operational settings and insufficient knowledge of feed-product balance. Material (Feedstock and Input Issues) such as feedstock variability, impurities, and catalyst deactivation further exacerbate off-gas levels. Additionally, Method (Processes and Procedures) play a role, with inefficient process flow designs, unstable reaction conditions, and deviations from ideal temperature or pressure compounding the problem.
ProSolvr, a GEN-AI-powered root cause analysis (RCA) application, provides petrochemical plants with a robust solution to these multifaceted challenges. By integrating a fishbone diagram (Ishikawa diagram) framework with Six Sigma principles, ProSolvr systematically categorizes potential causes across domains like Machine (Equipment Factors), addressing issues such as malfunctioning temperature controls, reactor fouling, and inefficient distillation columns. It also tackles Measurement (Monitoring and Control) gaps, including poor alarm systems, faulty gas flow meters, and inadequate real-time data analysis. ProSolvr’s advanced GEN-AI capabilities analyze interconnected factors, offering actionable insights to mitigate high off-gas production effectively.
What sets ProSolvr apart is its ability to address not just internal factors but also Environment (External Factors) like humidity and temperature extremes, as well as utility variations such as power supply instability. By identifying root causes and generating precise recommendations for corrective and preventive actions, ProSolvr empowers teams to reduce emissions, optimize processes, and achieve long-term operational excellence. With ProSolvr, petrochemical plants can transform high off-gas production challenges into opportunities for improved efficiency and sustainability.
Who can learn from the High Off-Gas Production template?
- Operations Managers: Operations managers can use the template to analyze production inefficiencies, optimize processes, and improve overall plant performance by addressing off-gas issues systematically.
- Process Engineers: Process engineers can identify technical flaws in reaction conditions or equipment performance, leveraging the template to design more stable and efficient processes.
- Maintenance Teams: Maintenance teams can pinpoint recurring equipment failures, such as reactor fouling or faulty sensors, and plan proactive maintenance strategies using the template insights.
- Training Coordinators: Training coordinators can use the template to identify skill gaps in operator knowledge and design targeted training programs to minimize human errors and improve troubleshooting capabilities.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Quality assurance professionals can utilize the template to investigate material variability, catalyst issues, and deviations in quality standards that contribute to high off-gas production.
- Environmental Compliance Officers: Environmental officers can focus on identifying and mitigating factors that lead to increased emissions, ensuring the plant meets regulatory requirements and reduces environmental impact.
Why use this template?
Using Six Sigma principles, a GEN-AI-driven root cause analysis with a quality and reliability tool like ProSolvr, focuses on reducing variability and enhancing process efficiency. Once the root causes are identified, suitable corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) can be implemented. The structured nature of a fishbone diagram ensures comprehensive exploration of potential causes, leaving no aspect of the operation unchecked. This not only enhances operational reliability but also aligns the plant’s performance with environmental and safety standards, ensuring sustainable operations.
By focusing on the root causes rather than surface-level symptoms, GEN-AI-powered RCA fosters long-term solutions, minimizing recurrence. Unlock effective root cause analysis with ProSolvr by smartQED to drive sustainable solutions and prevent future disruptions in your petrochemical plant.