Root Cause Analysis of Gearbox Noise and Vibration Issues
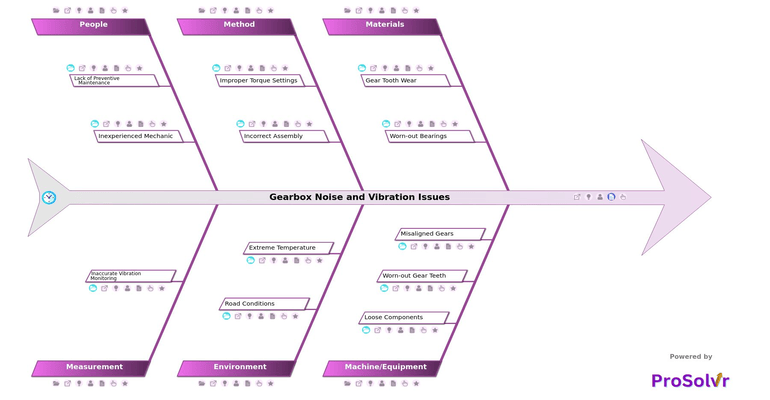
Gearbox noise and vibration are common concerns in automotive systems that can lead to discomfort for passengers and indicate potential mechanical problems. These issues may arise from misalignments, worn gears, bearing defects, improper lubrication, or structural issues like casing vibrations. Over time, the gearbox’s performance may degrade due to wear and tear, leading to noisy or vibrating operation.
Diagnosing the root cause of gearbox noise and vibration is critical; neglecting these issues can result in further damage, reduced efficiency, and higher maintenance costs. A fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa diagram, is a valuable tool for performing root cause analysis on gearbox issues. By categorizing potential causes, the fishbone diagram allows for a structured investigation, encouraging teams to brainstorm all possible factors that contribute to gearbox problems.
Once the root causes are identified, corrective actions can be planned and implemented. The RCA process can also reveal procedural or training gaps, leading to improvements in assembly methods or maintenance routines. Through systematic investigation and correction, the gearbox can be restored to optimal performance, reducing noise and vibration and extending the lifespan of the automotive system.
Who can learn from the Gearbox Noise and Vibration Issues template?
- Automotive Engineers: Benefit from understanding gearbox noise and vibration issues to diagnose and solve problems more efficiently, improving vehicle performance.
- Maintenance Technicians: Apply this template to systematically troubleshoot gearbox noise and vibration problems, leading to quicker and more accurate repairs.
- Quality Assurance Teams: Enhance inspection processes to catch potential noise and vibration issues early, reducing defects and warranty claims.
- Fleet Managers: Use insights from this template to train teams on preventive maintenance techniques, reducing downtime and extending fleet life.
- Automotive Training Instructors: Incorporate this template into the curriculum, helping students develop diagnostic skills for real-world challenges in automotive maintenance.
Why use this template?
Using a structured root cause analysis for gearbox noise and vibration issues can enhance the diagnostic process significantly. An AI-driven tool like ProSolvr facilitates efficient problem-solving techniques and effective collaboration among teams. ProSolvr enables a systematic approach to identifying potential causes of gearbox noise and vibration, encouraging comprehensive analysis. This accelerates troubleshooting, develops effective preventive strategies, and minimizes downtime, ultimately boosting overall gearbox performance and reliability.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effective diagnosis and resolution of all the gearbox issues, ensuring comfort and vehicle safety.