RCA of Eye Drop Recall in 2023
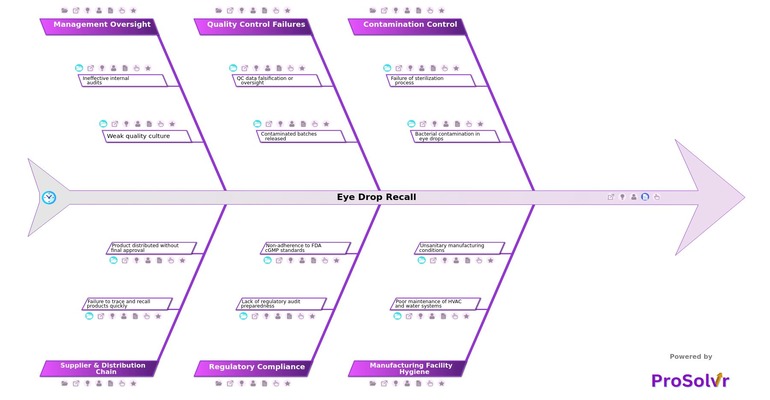
In May 2022, the CDC began tracking an unusual outbreak linked to preservative-free artificial tears. By February 2023, investigations confirmed the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa—a rare, drug-resistant strain (VIM-GES‑CRPA)—in opened bottles of EzriCare and Delsam Pharma eye drops, manufactured by Global Pharma Healthcare in Tamil Nadu, India. FDA inspections uncovered severe lapses in contamination control: failure of sterilization processes, inadequate cycle validation, and microbial contamination due to unsanitary manufacturing conditions and poor hygiene in cleanrooms, HVAC, and water systems, including suspected biofilm buildup in supply lines.
The public health impact was devastating. By March 2023, 68 patients across 16 U.S. states were affected—resulting in 3 deaths, 8 cases of vision loss, and 4 eye removals. Investigators also found that contaminated batches had been released, red flags in test results were overlooked, and quality control protocols were either inadequate or ignored. Reports indicated QC data oversight, insufficient microbial testing, and a broader failure in regulatory compliance—repeated cGMP violations, failure to act on prior FDA Form 483 observations, and a lack of preparedness for audits. Worse still, the distribution chain was compromised: products were shipped without final approval, and traceability gaps delayed the recall process.
In situations like this, a structured Root Cause Analysis (RCA) becomes critical—not only for identifying what went wrong, but for preventing recurrence and restoring confidence. Traditional RCA methods often struggle to organize findings across complex systems involving contamination, facility hygiene, quality assurance, and regulatory oversight. This is where ProSolvr adds significant value. As a Gen-AI assisted RCA platform, ProSolvr helps teams structure their investigations using industry-standard frameworks like fishbone diagrams, Six Sigma, and 5 Whys, enabling a clear, categorized view of contributing factors across areas like internal audits, sterilization failures, supplier breakdowns, and management oversight.
ProSolvr supports faster, more reliable investigations by making root causes easier to visualize, connect, and communicate. It enables teams to document second-level causes, align findings with regulatory expectations, and create audit-ready CAPA outcomes with greater consistency. By turning complexity into clarity, ProSolvr empowers pharmaceutical organizations to respond decisively, comply confidently, and build stronger systems that prevent future breakdowns.
Who can learn from the Batch Rejection template?
- Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Teams: To understand how failures in sterilization, hygiene, and data oversight can lead to product recalls, and to improve internal QA protocols and compliance mechanisms.
- Regulatory Affairs Professionals:To analyze where regulatory non-compliance occurred and how to enhance preparedness for FDA audits, 483 observations, and cGMP adherence.
- Manufacturing Operations Managers: To learn how poor facility hygiene and process control can lead to contamination, and how preventive maintenance and operational oversight are critical.
- R&D and Product Development Teams: To identify design and formulation vulnerabilities that might increase contamination risk, and to factor regulatory and safety expectations into product development.
- Corporate Risk and Compliance Officers:To use the RCA as a case study for assessing enterprise-level risks, improving audit frameworks, and implementing CAPA systems across departments.
- Suppliers and Contract Manufacturers: To understand the consequences of weak distribution controls and poor traceability, and to adopt best practices in product release and supply chain integrity.
Why use this template?
The eye drop recall case highlights how contamination, compliance failures, and systemic oversights can converge into a high-impact crisis. ProSolvr provides a structured, visual workspace that helps teams conduct thorough Root Cause Analysis using fishbone diagrams aligned with Six Sigma and 5 Whys methodologies. It enables teams to clearly map out interconnected causes—such as sterilization breakdowns, cleanroom hygiene issues, or failures in audit response—ensuring that investigations are both comprehensive and traceable.
By guiding users through a consistent RCA process, ProSolvr reduces ambiguity, reinforces regulatory compliance, and helps standardize problem-solving across teams. It transforms complex investigations into well-documented, collaborative analyses that support stronger corrective and preventive actions (CAPA). With ProSolvr, pharmaceutical organizations can institutionalize quality, reduce the risk of recurrence, and respond more confidently to regulatory scrutiny.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to resolve issues in your organization—clearly, confidently, and consistently.