Root Cause Analysis of Delayed Vehicle Deliveries
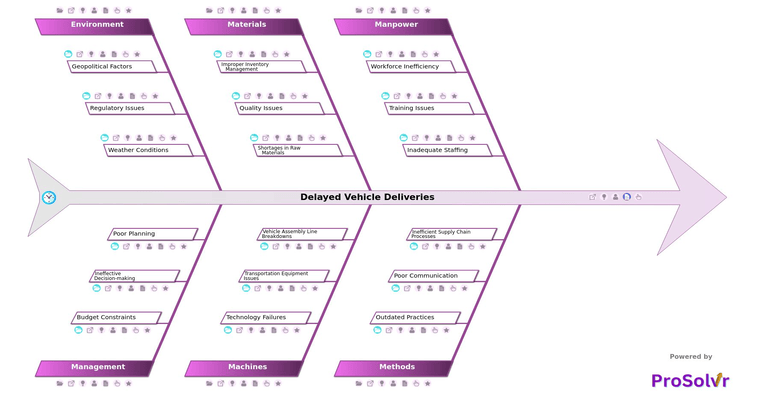
Delayed vehicle deliveries are a critical challenge in the automotive industry, often resulting from disruptions across manpower, methods, materials, machines, environment, and management. These delays create a ripple effect throughout the supply chain, impacting production schedules, dealer commitments, and customer satisfaction. The consequences can be severe—lost revenue, damaged brand reputation, increased operational costs, and strained relationships with suppliers and customers. Without a structured approach to identifying and eliminating root causes, these delays can become recurring, leading to long-term inefficiencies.
For instance, inadequate staffing due to recruitment challenges, lack of skilled workers, and high absenteeism can slow down both production and logistics. Outdated skills and insufficient training programs further exacerbate workforce inefficiencies, leading to delays in vehicle assembly and shipment. Additionally, manual tracking of logistics, lack of automation, and delayed updates to stakeholders create communication bottlenecks, making it difficult to coordinate deliveries effectively. Inefficient supply chain processes, such as customs clearance delays and ineffective route planning, further compound the problem.
Material-related issues also contribute significantly to delayed vehicle deliveries. Global material shortages, supplier delays, and inaccurate inventory forecasting can disrupt production timelines. Substandard raw materials and defective parts lead to quality issues, often requiring rework or replacement, which further extends delivery schedules. Aging delivery vehicles, insufficient fleet capacity, and IT system downtimes add additional layers of complexity, slowing down transportation efficiency. On the production side, vehicle assembly line breakdowns due to obsolete machinery and poor maintenance schedules frequently lead to unplanned stoppages, affecting overall throughput.
To address these challenges, manufacturers and supply chain teams need a structured visual Root Cause Analysis (RCA) application powered by Gen AI, such as ProSolvr. Rather than relying on reactive troubleshooting, ProSolvr enables teams to systematically analyze failures using Fishbone Diagrams, categorizing issues under workforce inefficiencies, supply chain disruptions, material shortages, and machine failures. By identifying root causes such as ineffective decision-making, unrealistic timelines, lack of contingency planning, or insufficient investment in logistics, organizations can implement targeted Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA). With ProSolvr’s structured problem-solving approach, manufacturers can enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce bottlenecks, and improve overall delivery reliability, ensuring that delays are not just managed—but systematically prevented.
Who can use the Delayed Vehicle Deliveries template?
- Supply Chain and Logistics Teams: These teams are responsible for managing inventory, transportation, and coordination with suppliers. They can use the RCA template to identify issues such as inefficient supply chain processes, delays in customs clearance, or ineffective route planning and develop corrective actions to streamline delivery timelines.
- Production and Operations Managers: Managers overseeing vehicle assembly lines and factory operations can use the RCA template to address problems like obsolete machinery, poor maintenance schedules, and inadequate staffing. This helps ensure smooth production flows and minimizes disruptions affecting deliveries.
- Quality Assurance Teams: QA teams can use the RCA template to analyze delays caused by quality issues such as substandard raw materials or defective parts. They can develop measures to improve supplier quality checks and enhance product consistency.
- Human Resources and Training Departments: HR teams can use the template to address manpower-related challenges like high absenteeism, outdated skills, and insufficient training programs. By identifying these root causes, they can introduce better hiring strategies, improve training initiatives, and foster workforce efficiency.
- Executive Management and Strategic Planners: Senior leaders and decision-makers can leverage the RCA template to address broader issues such as budget constraints, ineffective decision-making, and lack of contingency planning. This allows them to align operational strategies with business goals and ensure sustainable improvements in the delivery process.
Why use this template?
GEN-AI-powered root cause analysis, supported by tools like ProSolvr, enables the automobile industry to address the complexities of delayed vehicle deliveries effectively. By systematically identifying root causes and implementing robust CAPA measures, organizations can mitigate future risks, improve customer satisfaction, and strengthen their competitive edge. With its intuitive interface, teams can document insights, track progress, and ensure accountability for implementing solutions, leading to measurable improvements in delivery timelines and overall operational efficiency.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effectively mitigating risks in your automobile plant.