Root Cause Analysis of Defective Welds in Chassis Assembly
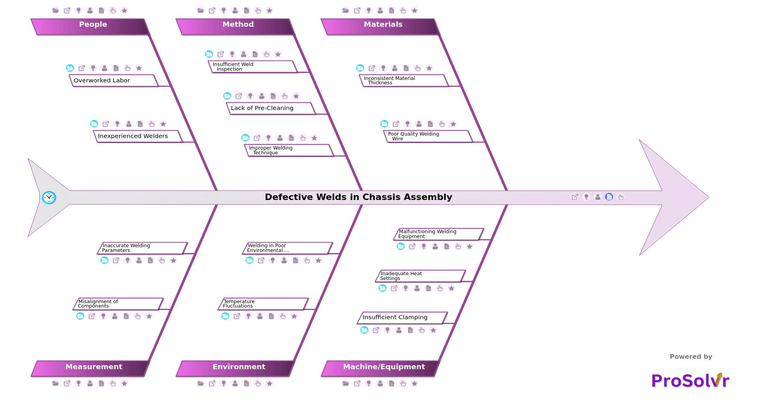
Defective welds in chassis assembly are a serious problem in car manufacturing. These defects can weaken the structure of vehicles, leading to safety risks, higher repair costs, and potential recalls. Common causes of defective welds include poor material quality, wrong welding settings, equipment issues, operator mistakes, and lack of proper process controls. These defects can show up as cracks, incomplete joins, or weak connections, which can cause failures during vehicle operation, especially in tough conditions like accidents or rough roads.
Fixing this issue is crucial for ensuring product quality, keeping customers safe, and following regulations. A root cause analysis (RCA) using a fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa diagram, can help identify and solve the underlying problems that lead to defective welds. This method breaks down the issue into key categories and helps track potential causes back to their source, allowing the team to focus on specific issues that need fixing.
By visualizing possible root causes in a fishbone diagram, teams can prioritize corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) more effectively. Corrective actions might include re-training workers, updating equipment maintenance plans, or changing process standards to ensure the best welding conditions. Preventive actions could involve stricter material inspections or real-time quality checks during welding. This structured approach not only fixes the immediate problem of defective welds but also helps create a stronger, quality-focused manufacturing process for the future.
Who can use the Defective Welds in Chassis Assembly template?
- Welding Technicians and Engineers: They can learn how factors like equipment settings and materials affect weld quality, helping them avoid common defects.
- Quality Control and Inspection Teams: These teams can improve their inspection techniques and monitoring to catch defects before vehicles leave the production line.
- Production Managers: By understanding the root causes of defective welds, managers can improve production workflows and ensure that teams have the right training and resources.
- Design and Manufacturing Engineers: They can learn how weld quality affects the overall performance and reliability of chassis, allowing them to design better components.
- Maintenance Teams: Knowing that defective welds may come from equipment issues helps these teams schedule better preventive maintenance for welding machines.
- Supply Chain and Procurement Teams: They can understand the importance of sourcing high-quality materials to prevent weld defects, leading to better supplier selection and material inspections.
Why use this template?
Using ProSolvr can significantly enhance how we manage defective welds in chassis assembly. This template assists teams in identifying the root causes of welding issues and offers practical solutions. When combined with Six Sigma principles, it makes the process more organized and efficient. ProSolvr helps teams monitor key performance metrics, identify areas for improvement, and recommend specific corrective and preventive actions. Ultimately, this leads to better weld quality and improved overall efficiency in the manufacturing process.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to efficiently analyze and resolve issues in your automotive manufacturing plant for improved outcomes.