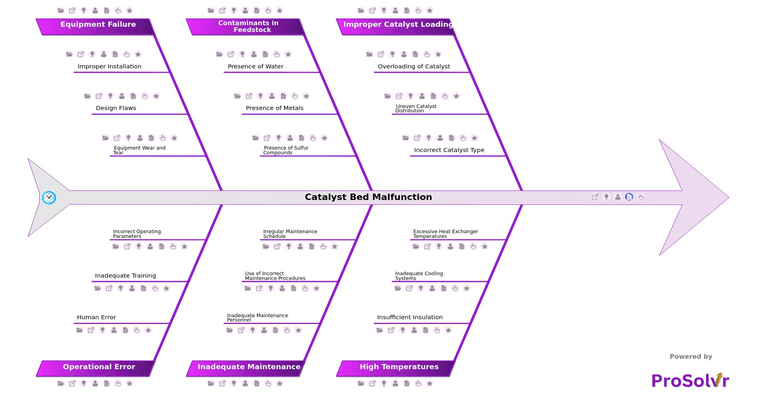
RCA of Catalyst Bed Malfunction
Catalyst beds play a vital role in petrochemical plants, enabling key chemical reactions by providing surfaces for reactants to interact. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps address catalyst bed malfunctions by identifying the actual causes rather than just the symptoms. A visual RCA might show that impurities in the feedstock cause catalyst poisoning, or that improper packing leads to channeling in the bed. By pinpointing these causes, plant operators can take corrective actions like improving feedstock quality, optimizing catalyst loading, or adjusting operating conditions to prevent sintering.
When catalyst beds malfunction, they can cause severe operational problems, including reduced reaction efficiency, unwanted side reactions, or complete process shutdowns. Common issues include catalyst poisoning, where contaminants deactivate the catalyst, channeling, which allows flow to bypass parts of the catalyst bed, and sintering, where high temperatures cause the catalyst particles to clump together. These problems result in lower product yields, higher energy consumption, and increased operational costs.
RCA tackles immediate issues and boosts long-term reliability and efficiency. Documenting findings and corrective actions helps build a knowledge base, preventing similar future problems. Continuous monitoring and periodic RCA can also spot emerging issues before they turn into major malfunctions. A fishbone diagram can serve as both a reactive and proactive tool, improving the stability and productivity of processes that rely on catalysts.
Who can learn from the Catalyst Bed Malfunction template?
- Process Engineers: They can understand the importance of proper catalyst loading, managing operational parameters, and ensuring correct design and installation of catalyst beds.
- Maintenance Technicians: They will learn the value of regular maintenance, accurate calibration, and thorough inspections to prevent equipment wear and tear.
- Operations Managers: They can see how human error, lack of training, and not following procedures affect the performance and reliability of catalyst beds.
- Safety and Compliance Officers: They will focus on monitoring environmental factors like temperature and contamination, ensuring adherence to safety protocols during catalyst bed operations.
- Quality Assurance Teams: They can ensure proper material selection, feedstock quality, and effective testing and validation to prevent malfunctions.
- Training and Development Coordinators: They will recognize the need for continuous training in catalyst handling, maintenance procedures, and operational parameter management to minimize malfunctions.
Why use this template?
This Gen-AI-powered root cause analysis helps identify the key issues behind catalyst bed failures, such as improper loading, equipment wear, or human error. By thoroughly analyzing these problems, organizations can implement corrective actions that not only fix the current issue but also prevent future ones. RCA boosts the reliability and efficiency of catalyst beds, reduces downtime, and ensures safer, more consistent production processes—leading to cost savings and improved performance.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for effectively analyzing the causes behind malfunctioning equipment in your organization.