Root Cause Analysis of Brake System Failures
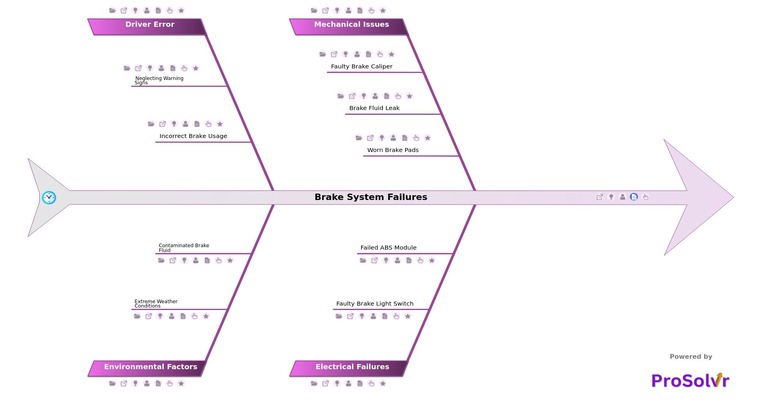
Brake system failure in passenger vehicles is a critical vehicle safety issue that can result from various mechanical, hydraulic, or electrical problems. Common causes of brake failure include worn-out brake pads, malfunctioning master cylinders, brake fluid leaks, or issues with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). Environmental factors like rust and corrosion, improper maintenance, and human errors, such as using the wrong type of brake fluid, can also lead to brake system failure. The consequences of such failures can be severe, resulting in vehicle accidents, injuries, or fatalities when the vehicle loses its ability to decelerate or stop effectively.
To address brake system failure efficiently, ProSolvr, a Generative AI-powered Root Cause Analysis tool, can be highly effective. By integrating AI with fishbone diagram analysis (also known as the Ishikawa diagram), ProSolvr helps categorize potential causes under broad headings, such as mechanical faults, hydraulic issues, and user errors. This structured approach ensures that all potential causes of brake failure are thoroughly examined. By using ProSolvr root cause analysis, automotive technicians and engineers can systematically investigate the factors contributing to brake system failures, improving both vehicle safety and reliability.
ProSolvr facilitates a collaborative team-based approach where all angles are considered, and no potential cause is overlooked. After identifying root causes using Six Sigma principles, corrective actions can be implemented, such as improving maintenance practices, driver education, or using higher-quality materials. Long-term, this helps reduce the likelihood of recurring brake failures, ultimately enhancing automotive safety and system reliability.
Who can learn from the Brake System Failures template?
- Automotive Technicians and Mechanics: Diagnose brake system issues efficiently to ensure accurate repairs and preventive maintenance.
- Automobile Manufacturers and Engineers: Analyze and enhance the design and durability of brake systems in new models, improving overall vehicle safety.
- Fleet Managers and Vehicle Maintenance Teams: Use this template to assess and maintain vehicle brake systems regularly, ensuring safety and minimizing downtime.
- Drivers and Vehicle Owners: Understanding the causes of brake failure through ProSolvr RCA can promote safer driving habits and encourage routine brake inspections, improving personal vehicle safety.
- Automotive Safety Inspectors and Regulators: Identify patterns in brake system failures across different vehicle types, supporting regulatory efforts to improve vehicle safety standards.
- Insurance Companies and Accident Investigators: Use ProSolvr RCA to assess brake failure causes in accidents, determining whether mechanical faults or human error contributed to the incident.
Why use this template?
Generative AI-powered root cause analysis (RCA), through tools like ProSolvr, revolutionizes how brake system failures are diagnosed and resolved. ProSolvr streamlines the troubleshooting process by enabling users to systematically investigate possible causes of brake failures using structured methods like fishbone diagrams and guided problem-solving techniques. This tool helps ensure that potential causes are not overlooked and encourages efficient collaboration. By simplifying and organizing the RCA process, ProSolvr helps prevent future brake system issues, improving overall vehicle safety through a more structured and efficient approach to root cause analysis.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to identify and resolve issues with automotives for safer driving.