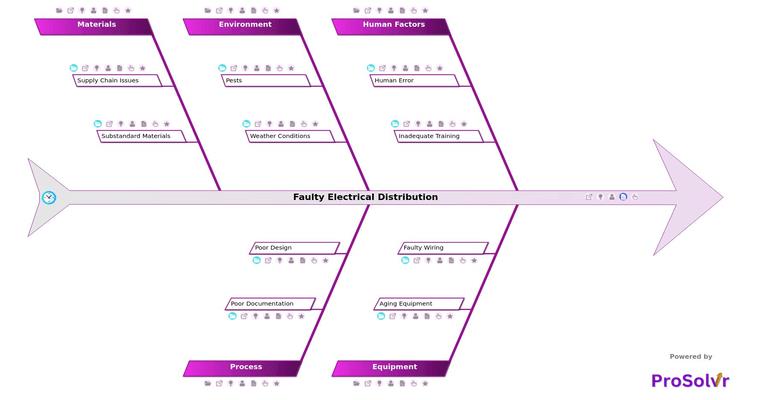
RCA of Faulty Electrical Distribution
Faulty electrical distribution refers to failures or inefficiencies in the systems responsible for transmitting and distributing electricity from generation sources to end users. In the energy domain, such issues can manifest as power outages, voltage fluctuations, equipment breakdowns, or even safety hazards like fires and electrocution. Problems often arise due to multiple interlinked causes, ranging from human mistakes and equipment degradation to environmental factors and poor processes.
For example, human error such as Incorrect Installation or mislabeling of components can lead to improper connections that compromise the integrity of the distribution system. Similarly, aging equipment or overloaded circuits can strain infrastructure, while environmental issues like rodent damage or extreme temperatures further degrade reliability. These failures not only impact operational efficiency but can also result in financial losses, safety incidents, and regulatory non-compliance.
When such incidents occur, a structured approach like root cause analysis (RCA) becomes critical in identifying the underlying factors rather than just addressing the surface-level symptoms. A GEN-AI powered RCA tool that leverages a fishbone diagram integrated with Six Sigma principles can be particularly effective. This comprehensive view enables a more thorough investigation into the underlying issues, facilitating a deeper understanding of how various factors interconnect and contribute to the problem.
Applications like ProSolvr bring additional value by combining GEN-AI with fishbone diagrams to simplify and accelerate the RCA process. ProSolvr allows teams to visually map incidents, assign categories, and collaborate effectively on identifying solutions. This ensures a structured CAPA plan that not only addresses immediate issues but also strengthens long-term reliability. By embedding Six Sigma rigor into the RCA process, ProSolvr empowers energy organizations to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive prevention, reducing risks, downtime, and costs associated with faulty electrical distribution.
Who can learn from the Faulty Electrical Distribution template?
- Electrical Engineers: They can utilize the template to diagnose and resolve technical issues, ensuring system reliability and efficiency.
- Maintenance Technicians: They can use it to identify recurring problems and implement effective maintenance strategies.
- Safety Managers: They can benefit by pinpointing potential hazards and developing safety protocols to prevent accidents.
- Quality Assurance Teams: They can analyze root causes of distribution faults to improve overall quality and performance, while project managers can oversee the implementation of corrective and preventive actions, ensuring project objectives are met and risks are mitigated.
- Students and Trainees: In electrical engineering and related fields, they can use the template as a learning tool to understand the complexities of electrical distribution systems and the importance of comprehensive problem-solving methodologies.
Why use this template?
The template can help in identifying and rectifying issues such as repairing faulty equipment or correcting human errors, to restore proper function and safety. It can also help in focusing on long-term solutions to prevent recurrence, such as enhancing training programs, improving maintenance schedules, and upgrading system designs. By systematically addressing these issues with a quality tool like ProSolvr, organizations can ensure a more reliable and efficient electrical distribution system, ultimately reducing downtime and improving safety.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to create your own templates for efficient problem analysis and resolution.