Root Cause Analysis of Defective Circuit Boards
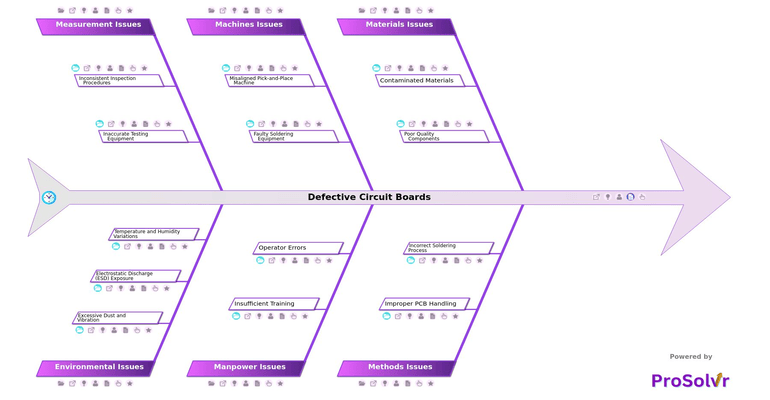
A high rate of defective circuit boards can slow down production, inflate rework costs, and weaken product reliability. Many failures begin with material issues such as contaminated materials, poor quality components, or incorrect specifications. Improper storage that exposes PCBs to dust, moisture, or oxidation further increases the likelihood of early failures. Supplier defects can silently slip into the line, creating widespread, hard-to-detect issues that disrupt even the most streamlined manufacturing processes. When these material-related problems go unchecked, they create a chain reaction that affects throughput, product consistency, and customer satisfaction.
During assembly, improper methods often amplify defects. Rough handling leads to physical damage, while a lack of ESD protection results in electrostatic discharge that permanently harms sensitive components. Soldering mistakes caused by insufficient flux application or incorrect temperature settings frequently produce weak joints, bridging, or intermittent failures. These method-level weaknesses are compounded by manpower challenges such as insufficient training, poor troubleshooting skills, and operator errors. When operators are not confidently equipped to handle PCBs or correctly set up machines, the likelihood of recurring defects grows quickly.
Machine-related factors remain another significant contributor to PCB failures. A misaligned pick-and-place machine, nozzle blockages, incorrect component placement, faulty soldering equipment, worn-out soldering tips, and inconsistent heat application can affect hundreds of boards within minutes. Measurement issues such as inconsistent inspection procedures, inaccurate testing equipment, false result patterns, and AOI calibration problems make it even harder to detect defects before they reach customers. These gaps allow defective boards to pass through the line undetected, creating avoidable scrap and warranty risks. Environmental influences such as excessive dust, vibration, temperature swings, humidity fluctuations, and poor grounding conditions further destabilize PCB reliability and impact soldering quality.
Organizations seeking long-term improvement turn to structured, intelligence-driven RCA to break the cycle of recurring failures. A GEN AI powered approach combined with fishbone diagrams and Six Sigma principles helps teams map issues across materials, methods, machines, manpower, measurement, and environment with remarkable clarity. ProSolvr brings this entire workflow into a powerful digital platform where engineers can uncover hidden causes and implement strong corrective and preventive actions. By integrating AI insights with proven RCA methodology, ProSolvr enables manufacturers to reduce PCB defects, accelerate investigations, and build a culture of consistent, high-quality production.
Who can learn from the Defective Circuit Boards template?
- Manufacturing Engineers: They can use the analysis to optimize production processes, refine soldering techniques, and ensure machine calibration to minimize defects. Understanding root causes helps them implement preventive measures and improve product quality.
- Quality Control Teams: By analyzing measurement and inspection issues, they can enhance defect detection methods, improve testing equipment calibration, and establish more consistent quality standards. This helps reduce false positives/negatives and ensures fewer defective boards reach customers.
- Supply Chain & Procurement Teams: They can use the findings to evaluate supplier quality, enforce stricter component specifications, and ensure proper material handling. This reduces risks associated with poor-quality components and contaminated materials.
- Production Line Operators: They gain insights into the importance of proper machine setup, correct soldering techniques, and careful PCB handling. Training based on the RCA helps them avoid common mistakes and maintain consistent production standards.
- Design Engineers: Learning from defects in manufacturing helps them design PCBs that are easier to produce, reducing misalignment issues, soldering difficulties, and susceptibility to environmental factors. This leads to better manufacturability and higher reliability.
- Maintenance & Equipment Technicians: They can identify recurring machine issues, such as misaligned pick-and-place equipment or faulty soldering stations, and implement proactive maintenance. This reduces unexpected downtime and ensures machines operate at peak efficiency.
Why use this template?
A high rate of defective circuit boards requires a clear and structured approach to find the real causes and fix them effectively. By completing a proper root cause analysis and then applying the right corrective and preventive actions, manufacturers can steadily reduce defects and improve overall product quality. This creates a continuous improvement cycle that strengthens processes and boosts efficiency across the production line.
ProSolvr makes this even easier by providing a collaborative platform where teams can analyze issues, document actions, and track improvements in one place. With GEN-AI powered RCA tools, ProSolvr helps identify root causes faster and supports more accurate and effective CAPA decisions.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED to solve problems efficiently and improve quality in your organization.