RCA of Compressor Failures
Compressor failures in petrochemical plants are significant because compressors are critical for maintaining the flow and pressure of gases across various processes. These failures can lead to unplanned shutdowns, reduced efficiency, and safety hazards. The disruption can also impact downstream processes, causing delays and inefficiencies throughout the production line. In some cases, compressor failures pose serious safety risks, potentially leading to hazardous leaks, fires, or explosions that endanger both personnel and equipment.
Consequences of Compressor Failure in Petrochemical Plants
Using a fishbone diagram for root cause analysis allows petrochemical plants to systematically address compressor failures by identifying and correcting the underlying issues. This approach not only resolves the immediate problem but also helps prevent future failures, improving overall plant reliability and safety. Additionally, a quality tool like ProSolvr fosters continuous improvement by providing valuable insights that can lead to enhanced maintenance practices, better equipment design, and improved operational procedures, ultimately contributing to the overall stability and profitability of the plant.
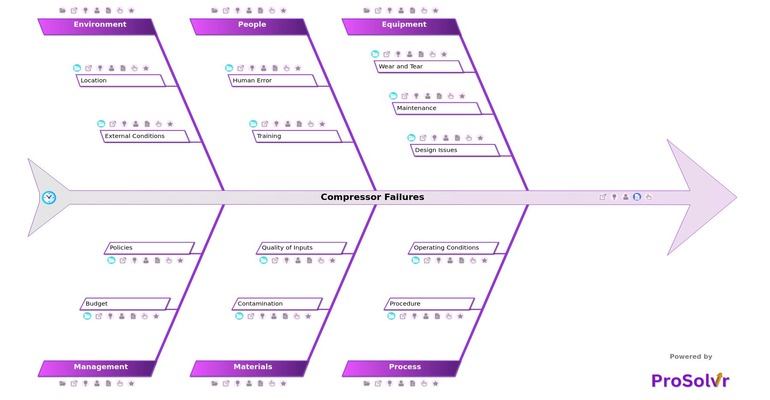
Compressor Failures
- Equipment
- Wear and Tear
- Rotor damage
- Bearing failure
- Maintenance
- Use of incorrect lubricants
- Lack of preventive maintenance
- Design Issues
- Improper selection of components
- Inadequate compressor design
- Process
- Procedure
- Improper startup/shutdown procedures
- Lack of standardized operating procedures
- Operating Conditions
- Incorrect operating pressure
- Overloading the compressor
- People
- Human Error
- Failure to follow maintenance protocols
- Incorrect handling of the compressor
- Training
- Lack of awareness of emergency procedures
- Insufficient operator training
- Materials
- Contamination
- Foreign particles in the lubrication system
- Contaminated intake air
- Quality of inputs
- Use of incompatible materials
- Substandard quality of lubricants
- Environment
- Location
- Proximity to corrosive chemicals
- Poor ventilation in the compressor room
- External Conditions
- Humidity causing corrosion
- High ambient temperature
- Management
- Budget
- Delayed investment in equipment upgrades
- Insufficient budget for spare parts
- Policies
- Lack of clear responsibility for compressor operation
- Inadequate maintenance schedules
Suggested Actions Checklist
This detailed checklist can guide the implementation of corrective, preventive, and investigative actions to address the potential causes of cracking furnace failure.
- External Factors
- Equipment
- Wear and Tear
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace worn-out components such as rotors and bearings.
- Repair or refurbish damaged parts to restore functionality.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a scheduled maintenance program to monitor and address wear and tear.
- Use high-quality, durable components to extend the lifespan of the compressor.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze wear patterns to identify root causes.
- Review maintenance records and operating conditions for contributing factors.
- Rotor Damage
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace or repair damaged rotors.
- Inspect the compressor for additional damage caused by rotor failure.
- Preventive Actions:
- Monitor rotor conditions regularly and perform routine inspections.
- Ensure proper installation and alignment of rotors to prevent damage.
- Investigative Actions:
- Examine the causes of rotor damage, such as excessive load or foreign particles.
- Review design and operational procedures to identify any design flaws.
- Bearing Failure
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace failed bearings and check for additional damage.
- Address any issues causing bearing failure, such as misalignment or inadequate lubrication.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a regular bearing inspection and lubrication schedule.
- Use high-quality bearings appropriate for the operating conditions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze bearing failure modes to determine root causes.
- Review maintenance logs to identify any missed maintenance tasks.
- Wear and Tear
- Maintenance
- Use of Incorrect Lubricants
- Corrective Actions:
- Drain and replace incorrect lubricants with the proper type.
- Clean the lubrication system to remove contaminants.
- Preventive Actions:
- Ensure proper lubricant selection and handling procedures are followed.
- Educate staff on the importance of using correct lubricants.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review lubricant specifications and supplier information.
- Analyze incidents where incorrect lubricants were used to determine how errors occurred.
- Lack of Preventive Maintenance
- Corrective Actions:
- Implement overdue preventive maintenance tasks.
- Review and address any issues identified during the maintenance.
- Preventive Actions:
- Establish and adhere to a comprehensive preventive maintenance schedule.
- Train personnel on the importance and procedures for preventive maintenance.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review past maintenance records to identify gaps and missed tasks.
- Analyze the impact of missed maintenance on compressor performance.
- Use of Incorrect Lubricants
- Design Issues
- Improper Selection of Components
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace improperly selected components with those that meet design specifications.
- Review and correct any system design issues affecting component compatibility.
- Preventive Actions:
- Ensure component selection is based on thorough design analysis and specifications.
- Use reputable suppliers and verify component specifications before purchase.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze component failure data to identify design issues.
- Review design and selection processes to prevent future occurrences.
- Inadequate Compressor Design
- Corrective Actions:
- Modify or replace the compressor design to meet operational requirements.
- Address any immediate issues caused by the design inadequacy.
- Preventive Actions:
- Conduct thorough design reviews and simulations before implementation.
- Regularly evaluate compressor performance and design to ensure ongoing suitability.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze design failures to identify root causes.
- Review design changes and updates for impact on performance.
- Improper Selection of Components
- Equipment
- Process
- Procedure
- Improper Startup/Shutdown Procedures
- Corrective Actions:
- Review and correct startup and shutdown procedures as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Train personnel on proper procedures and monitor compliance.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop and enforce standardized startup and shutdown procedures.
- Implement automated systems to ensure correct procedures are followed.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review incidents related to improper procedures to identify root causes.
- Analyze procedure documentation for completeness and accuracy.
- Lack of Standardized Operating Procedures
- Corrective Actions:
- Develop and implement standardized operating procedures (SOPs).
- Train all relevant personnel on the new SOPs and monitor adherence.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly review and update SOPs to reflect best practices and changes in technology.
- Conduct periodic audits to ensure SOP compliance.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze incidents or failures related to SOP deficiencies.
- Review existing procedures and identify areas for improvement.
- Improper Startup/Shutdown Procedures
- Operating Conditions
- Incorrect Operating Pressure
- Corrective Actions:
- Adjust operating pressure to within the recommended range.
- Inspect and repair any damage caused by incorrect pressure.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement pressure monitoring systems and alarms to maintain correct levels.
- Regularly calibrate pressure gauges and control systems.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review incidents of pressure deviations to identify causes.
- Analyze control system performance to ensure pressure settings are accurate.
- Overloading the Compressor
- Corrective Actions:
- Reduce operational loads to within the compressor's capacity.
- Repair any damage caused by overloading.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement load monitoring systems to prevent overloading.
- Regularly review load conditions and adjust as needed to avoid excessive loads.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze load data and operating conditions leading to overloading.
- Review system design and load management practices for improvements.
- Incorrect Operating Pressure
- Procedure
- People
- Human Error
- Failure to Follow Maintenance Protocols
- Corrective Actions:
- Review and address any missed maintenance tasks.
- Retrain personnel on correct maintenance protocols.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement checks and balances to ensure adherence to maintenance protocols.
- Use automated systems to remind and verify maintenance tasks.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze incidents related to maintenance protocol failures.
- Review training programs and adherence to procedures.
- Incorrect Handling of the Compressor
- Corrective Actions:
- Address any damage caused by improper handling.
- Implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Preventive Actions:
- Provide comprehensive training on proper handling procedures.
- Implement clear guidelines and labeling for compressor handling.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review incidents of improper handling to determine root causes.
- Evaluate training and handling procedures for improvements.
- Failure to Follow Maintenance Protocols
- Training
- Lack of Awareness of Emergency Procedures
- Corrective Actions:
- Conduct emergency response drills and provide training on procedures.
- Review and update emergency response plans as needed.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement regular emergency response training and drills.
- Ensure that all personnel are familiar with emergency procedures.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze past emergencies to assess the effectiveness of response procedures.
- Review training records and emergency response plans for completeness.
- Insufficient Operator Training
- Corrective Actions:
- Provide additional training for operators on compressor operation and maintenance.
- Assess and address any knowledge gaps.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop and implement a comprehensive training program for all operators.
- Include regular refresher courses and updates on new procedures or equipment.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review training records and performance evaluations to identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze incidents related to operator errors to determine training needs.
- Lack of Awareness of Emergency Procedures
- Human Error
- Material
- Contamination
- Foreign Particles in the Lubrication System
- Corrective Actions:
- Clean and replace contaminated lubrication system components.
- Implement filtration systems to prevent future contamination.
- Preventive Actions:
- Regularly inspect and maintain the lubrication system to avoid contamination.
- Use high-quality filters and ensure proper handling of lubricants.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the source of contamination to prevent recurrence.
- Review lubrication system maintenance practices and identify improvements.
- Contaminated Intake Air
- Corrective Actions:
- Clean or replace air filters and inspect the intake system.
- Address any issues causing contamination of intake air.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement air filtration and monitoring systems to ensure clean intake air.
- Regularly inspect and maintain air filters and intake systems.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review contamination incidents to identify sources and contributing factors.
- Evaluate air filtration systems and maintenance practices.
- Foreign Particles in the Lubrication System
- Quality of Inputs
- Use of Incompatible Materials
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace incompatible materials with those suitable for the compressor.
- Inspect and address any damage caused by the use of incorrect materials.
- Preventive Actions:
- Ensure proper material selection and compatibility before use.
- Implement quality control checks for all materials.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze incidents involving material incompatibility to determine root causes.
- Review material selection processes and specifications.
- Substandard Quality of Lubricants
- Corrective Actions:
- Replace substandard lubricants with high-quality alternatives.
- Clean the lubrication system to remove residues of substandard lubricants.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a quality assurance program for lubricant selection and handling.
- Regularly review and update lubricant specifications and suppliers.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the impact of substandard lubricants on compressor performance.
- Review lubricant quality control processes and supplier performance.
- Use of Incompatible Materials
- Contamination
- Environment
- Location
- Proximity to Corrosive Chemicals
- Corrective Actions:
- Relocate the compressor or implement protective measures to minimize exposure.
- Repair any damage caused by corrosive chemicals.
- Preventive Actions:
- Evaluate the location and implement barriers or protective coatings to reduce chemical exposure.
- Regularly inspect for signs of corrosion and address issues promptly.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the impact of chemical exposure on compressor performance.
- Review facility layout and chemical handling procedures for improvements.
- Poor Ventilation in the Compressor Room
- Corrective Actions:
- Improve ventilation by installing or repairing ventilation systems.
- Address any issues caused by poor ventilation, such as overheating.
- Preventive Actions:
- Ensure adequate ventilation in all compressor rooms.
- Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation systems.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review ventilation system performance and its impact on compressor operation.
- Analyze incidents related to poor ventilation and identify corrective actions.
- Proximity to Corrosive Chemicals
- External Conditions
- Humidity Causing Corrosion
- Corrective Actions:
- Address corrosion issues and implement measures to prevent further damage.
- Improve environmental controls to reduce humidity levels.
- Preventive Actions:
- Use corrosion-resistant materials and coatings for compressor components.
- Implement dehumidification systems or controls in areas prone to high humidity.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the impact of humidity on compressor components.
- Review environmental control measures and their effectiveness.
- High Ambient Temperature
- Corrective Actions:
- Implement cooling measures to reduce ambient temperature in the compressor room.
- Repair any heat-related damage to the compressor.
- Preventive Actions:
- Use cooling systems or air conditioning to maintain optimal temperature.
- Regularly monitor and manage ambient temperature conditions.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the impact of high temperatures on compressor performance.
- Review temperature control systems and their effectiveness.
- Humidity Causing Corrosion
- Location
- Management
- Budget
- Delayed Investment in Equipment Upgrades
- Corrective Actions:
- Prioritize and implement necessary equipment upgrades as soon as possible.
- Address any issues caused by outdated equipment.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop and adhere to a capital investment plan for equipment upgrades.
- Regularly review and update the budget to ensure timely investments.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review the impact of delayed upgrades on compressor performance and reliability.
- Analyze budgeting and investment processes to identify improvements.
- Insufficient Budget for Spare Parts
- Corrective Actions:
- Allocate additional funds to ensure adequate spare parts inventory.
- Address any issues caused by the lack of available spare parts.
- Preventive Actions:
- Develop and maintain a spare parts inventory management plan.
- Regularly review spare parts needs and budget accordingly.
- Investigative Actions:
- Analyze the impact of spare parts shortages on compressor performance.
- Review inventory management practices and budget allocation.
- Delayed Investment in Equipment Upgrades
- Policies
- Lack of Clear Responsibility for Compressor
Operation
- Corrective Actions:
- Define and assign clear responsibilities for compressor operation and maintenance.
- Communicate responsibilities to all relevant personnel.
- Preventive Actions:
- Implement a structured policy framework outlining roles and responsibilities.
- Regularly review and update policies to ensure clarity and effectiveness.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review incidents related to unclear responsibilities to identify improvements.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of current policies and communication strategies.
- Inadequate Maintenance Schedules
- Corrective Actions:
- Develop and implement a comprehensive maintenance schedule.
- Address any missed maintenance tasks and their impacts on compressor performance.
- Preventive Actions:
- Establish a regular and detailed maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations.
- Monitor adherence to the maintenance schedule and adjust as needed.
- Investigative Actions:
- Review past maintenance records to identify gaps and missed tasks.
- Analyze the impact of inadequate maintenance schedules on compressor reliability.
- Lack of Clear Responsibility for Compressor
Operation
- Budget
Who can learn from the Compressor Failures template?
- Maintenance Engineers and Technicians:
- Proper maintenance practices, understanding wear and tear, handling of lubricants, and responding to equipment failures.
- Improved skills in identifying, troubleshooting, and preventing compressor issues, leading to enhanced equipment reliability and reduced downtime.
- Operations Managers:
- Optimization of operating procedures, managing operating conditions, and understanding the impact of compressor performance on overall plant operations.
- Better decision-making and process management to ensure smooth and efficient plant operations.
- Process Engineers
- Integration of compressors into process systems, process control, and the impact of operational procedures on compressor performance.
- Enhanced ability to design and optimize processes that ensure compressors operate within their designed parameters and improve overall process efficiency.
- Safety Officers:
- Safety protocols related to compressor operations, emergency response procedures, and handling of hazardous materials.
- Strengthened safety measures and preparedness to manage and mitigate risks associated with compressor failures.
- Training and Development Specialists:
- Development of effective training programs, understanding the technical aspects of compressor operation and maintenance, and creating educational materials.
- Improved training programs that enhance the knowledge and skills of staff, leading to better management of compressor-related issues.
Why use this template?
A Gen-AI powered root cause analysis (RCA) of compressor failures in petrochemical plants is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability, safety, and efficiency of operations. By systematically identifying the underlying causes of failures, RCA allows plant operators to address not just the symptoms but the actual sources of problems, preventing recurrence and mitigating risks. This proactive approach helps in reducing unplanned downtime, minimizing costly repairs, and ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
Use ProSolvr by smartQED for efficiently resolving compressor issues and similar problems with your equipment in your petrochemical plant.