RCA of Boiler Failures
Boiler failures in petrochemical plants can lead to significant operational disruptions, safety hazards, and financial losses. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a critical tool for addressing these failures. By systematically investigating the underlying causes of a breakdown, RCA identifies not just the immediate reasons but also deeper, systemic issues contributing to the problem.
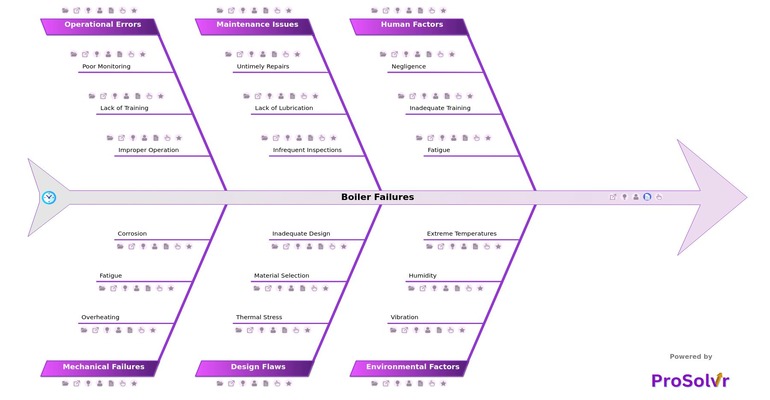
These failures can occur due to various factors such as material fatigue, corrosion, improper maintenance, and operational errors. When a boiler fails, it can result in unexpected plant shutdowns, halting production. This disruption not only affects output but also poses safety risks to workers, including potential hazards like explosions, fires, or the release of toxic substances. Furthermore, the costs associated with repairing or replacing a failed boiler, combined with lost production time, can be substantial.
One of the most effective methods for conducting RCA is the fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa diagram. This visual tool categorizes potential causes into distinct domains, allowing teams to map out all possible causes in a structured manner. By focusing investigations on the most likely root causes rather than just the symptoms, teams can effectively identify underlying issues. Once the root causes are determined, corrective and preventive actions can be implemented. This enables petrochemical plants to not only resolve immediate problems but also take proactive steps to prevent future failures, ultimately improving overall plant reliability and safety.
Who can learn from the Boiler Failures template?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) of Boiler Failures provide valuable insights for various stakeholder
- Plant Operations Managers: They can use the template to better understand the causes of boiler failures and implement measures to prevent similar issues, ensuring smoother and safer plant operations.
- Maintenance Teams: This group can learn about the importance of timely repairs, regular inspections, and proper lubrication, which are critical in preventing boiler failures and maintaining equipment longevity.
- Safety and Risk Management Personnel: Safety teams can use the template to identify potential hazards related to boiler failures and develop safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with human factors, environmental conditions, and operational errors.
- Design Engineers: Engineers involved in the design and selection of materials for boilers can benefit from understanding the design flaws that contribute to failures, enabling them to improve designs and select materials that better withstand operational stresses.
- Training Coordinators: Training coordinators can use the template to identify areas where staff may need additional training, such as proper operation and monitoring of boilers, to reduce the likelihood of operational errors and human factors leading to failures.
Why use this template?
Gen-AI powered root cause analysis using a quality tool like ProSolvr can be crucial for addressing boiler failures in petrochemical plants. It can systematically identify the underlying causes of failures rather than just treating the symptoms. By categorizing potential causes into domains, the diagram provides a clear and structured approach to pinpointing the root causes. This enables plant management to implement targeted corrective and preventive measures, reducing the risk of future failures, enhancing safety, and improving overall operational efficiency.
Draft and create a template for problem analysis in ProSolvr by smartQED.